One of the most important features of the Spring framework is its modularity. It is not one big monolith framework. What is the architecture of Spring Framework? What are Spring Modules? How are they organized?
You will learn
- What is the architecture of Spring Framework?
- How is Spring Framework Modularized?
- What are different Spring Modules?
- Which modules provide which Spring Features like Dependency Injection and Auto wiring?
- How can you develop applications with multiple layers with Spring?
Spring Architecture and Modules
Let’s look at the modules that are present in a typical Spring Project.
It is not organized as one big JAR file. It is composed of a large number of smaller JAR files.
Spring is organized into modules. Here is how Spring is organized conceptually:
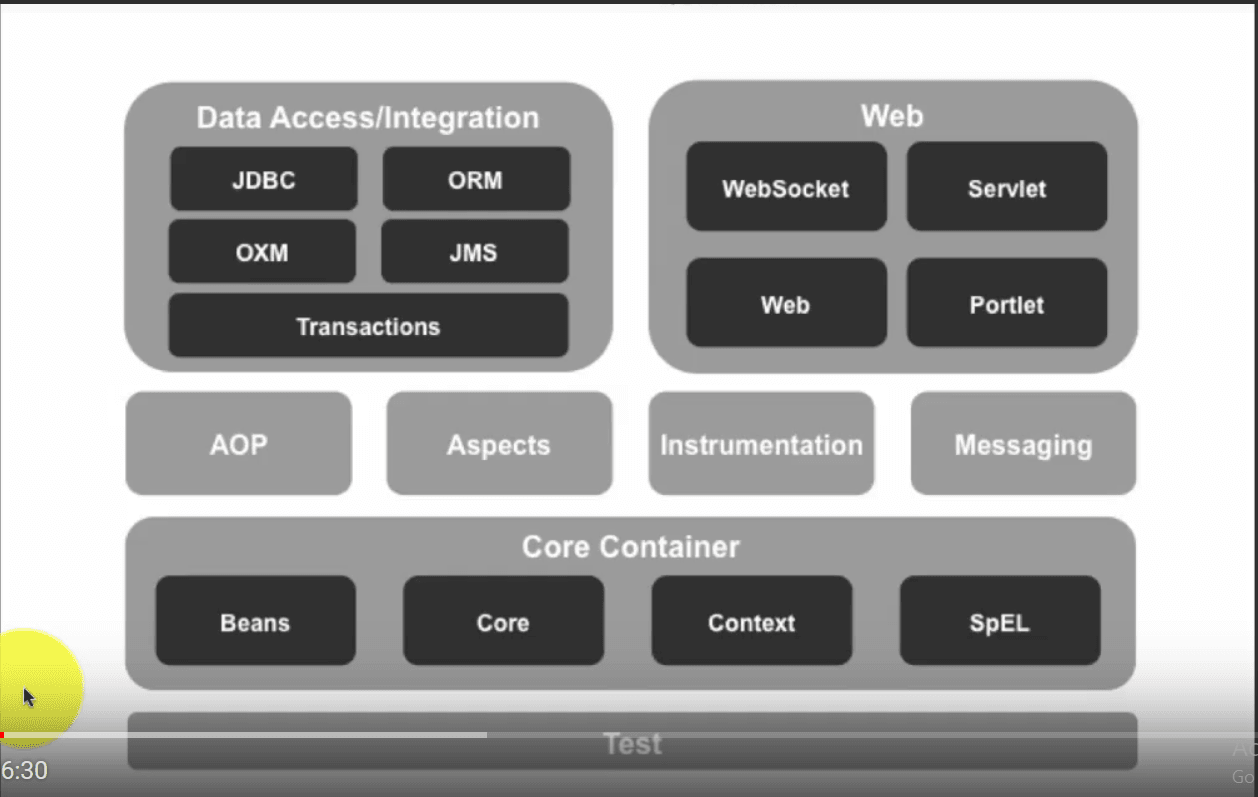
Container
This is the most heavily used part of the Spring framework. This includes modules such as:
- Beans: To manage the application dependencies
- Core
- Context: To maintain the application context
Database Access And Integration
Spring provide excellent options for implementing data and integration layers.
The important data access modules are:
- JDBC : To talk to relational database using JDBC
- ORM : Provides good integration with all ORM (Object Relational Mapping) frameworks, such as Hibernate and MyBatis.
- JMS : If you want to talk to another application over a queue, JMS provides an excellent option. Spring has good integration with JMS.
- OXM : This module provides good integration in scenarios where object to XML mappings are required.
- Transactions : Transaction management is an important part of data access integration functionality. Ideally, you want the transaction to be fully successful, or completely rolled back. If a transaction has 4 steps and failed at the third step, the previous two successful steps must also be rolled back. Spring has great support for transaction management.
Web
Spring has very good support to develop your web layer:
- Spring MVC : It is Spring’s own web framework
- Struts : Spring provides good integration with Struts.
Cross Cutting Features
An application is typically developed in multiple layers. For example, a web application is often designed to have three layers: web, business and data:
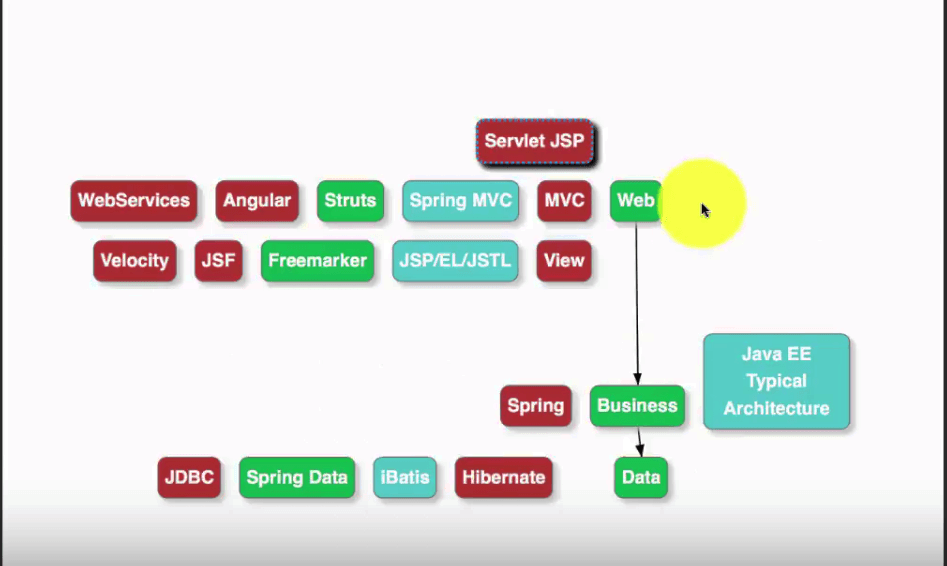
There are many things that are applicable to more than one layer. Those are called cross cutting concerns.
Unit Testing
One important cross cutting concern is unit testing. We want to be able to unit test code in all the three layers mentioned above. Spring Test framework provides good support for unit testing.
AOP
AOP stands for Aspect oriented programming. This module is useful for implementing features such as security and logging. Spring AOP provides basic AOP features.
Spring provides good integration with the AspectJ framework to do advanced AOP.
Summary
In this article, we had a brief look at the modular structure of the Spring framework. It is not a single monolith, but is organized as a set of small modules.
Spring Framework
This is the first article in a series of articles on Spring Framework:
- 1 - Introduction To Spring Framework
- 2 - What Is A Dependency?
- 3 - What Is Dependency Injection?
- 4 - What Is Component Scan?
- 5 - Architecture of Spring Framework - Modularity and Spring Modules
- 6 - What Are Spring Projects?
- 7 - Introduction To Spring Batch
