Spring framework identifies the beans and their dependencies, creates the beans and injects the dependencies into beans. How does the Spring Framework know where to search for beans and dependencies? How does Spring Boot make component scan easier?
You will learn
- Why do we need Component Scan in Spring?
- How can you configure a Component Scan in Spring with XML and Java Annotation based configuration?
- How does Spring Boot provide an automatic Component Scan?
- How do you solve problems with Component Scan?
In this article, we understand a little bit about component scan in the context of the Spring framework. We also see how component scan works with the Spring Boot framework.
Functionality Of The Spring Framework?
What is the fundamental functionality of the Spring framework? It is dependency injection.
Spring framework identifies the beans and their dependencies, finds them and injects the dependencies into beans.
Have a look at the following example:
@Component
public class ComplexAlgorithmImpl {
@Autowired
privare SortAlgorithm sortAlgorithm;
//...
}
public interface SortAlgorithm {
public int[] sort(int[] numbers);
}
@Component
public class QuickSortAlgorithm implements SortAlgorithm {
//...
}
Let’s quickly look at what Spring Framework needs to do get the autowiring working.
Spring framework needs to create instances of ComplexAlgorithmImpl and QuickSortAlgorithm.
Since QuickSortAlgorithm is the only implementation of SortAlgorithm available, it needs to be auto-wired into the sortAlgorithm field of ComplexAlgorithmImpl.
How Does Spring Search For Beans?
Let’s look at a few questions?
- How does Spring know where to look for the beans?
- How does it know where it needs to search for classes with annotations such as
@Componentand@Service?
A typical application could have hundreds of JARS, and as a result, thousands of classes. Therefore, it is not practical for Spring to search in all the classes present in the CLASSPATH.
Enter Component Scan
Clearly, Spring needs to be given inputs to identify the packages of the beans and dependencies. This is where component scan comes into the picture.
You declare a component scan by passing in a list of packages where the scan needs to take place:
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackages = {
"com.girishgodage.spring.example1.businessservice",
"com.girishgodage.spring.example1.dataservice.stub"})
class SpringContext {
}
The packages mentioned above are the locations where the beans and their dependencies are defined. This @ComponentScan gives a clue to the Spring framework on where to search.
Component Scan With XML Configuration
The thing is, component scan an also be done with XML configuration:

For this, use the <context:component-scan> tag, and specify the packages that are the locations.
How does Auto Configuration work with Spring Boot?
Spring Boot tries to automate a lot of stuff. Consider the code example below:
package com.girishgodage.spring.basics.springin5steps;
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringIn5StepsApplication {
//...
}
package com.girishgodage.spring.basics.springin5steps;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class SpringIn5StepsApplicationTests {
//...
}
As soon as Spring Boot sees the annotation @SpringBootApplication, it does an automatic scan on the current package, which is com.girishgodage.spring.basics.springin5steps.
You don’t need to explicitly define a component scan. If all the components that you need are present in the same package as SpringIn5StepsApplication, you don’t need to explicitly specify component scan.
Troubleshooting Component Scan In Spring Boot
Have a look at the following Spring Boot application:
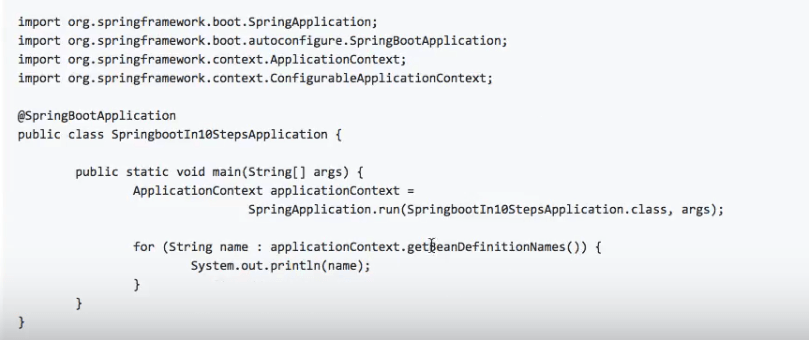
Since SpringbootIn10StepsApplication has a @SpringBootApplication annotation attached to it, an automatic component scan in the package com.girishgodage.springboot.basics.springbootin10steps, and all its sub-packages.
However, what would happen if you have one of the components defined in a different package, say com.in28mnutes.springboot.somethingelse?
In this case, you need to add that package to the component scan. There are a couple of options available for doing this.
Explicit Component Scan In Spring Boot
There are two ways of doing an explicit component scan:
Scan a parent package
This would scan the entire parent package tree of com.girishgodage.springboot.
@ComponentScan("com.girishgodage.springboot")
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringBootApllicationIn10Steps {
//...
}
Define explicit scans
In this case, we explicitly mention a list of specific packages within the tree. Therefore, only those two paths in the package tree will now get scanned.
@ComponentScan({
"com.girishgodage.springboot.basics.springbootin10steps",
"com.girishgodage.springboot.somethingelse"})
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringBootApllicationIn10Steps {
//...
}
As soon as you explicitly define a component scan, you are taking complete control. The default automatic scan that generally happens with Spring Boot will not longer take place. You need to specify the default package, as well as other packages.
Errors Related To Component Scan
Let’s look at some of the errors related to component scan and how you can solve them.
Typical Errors
When the controllers are not scanned, the URLs would not work. You would observe behaviors like this:
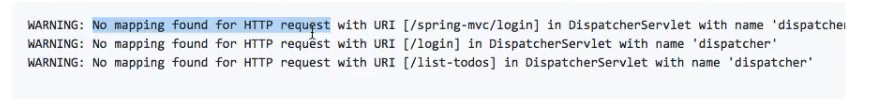
The other kind of error is when Spring does not find the dependencies. A typical error looks like this:

This means Spring expects at least one bean to auto-wire a dependency, but is not able to locate them.
Solving Errors With Component Scan
Here are some of the things to look fo:
- Make sure that you have the right annotation for the concerned bean -
@Controller,@Repository,@Component. - Make sure that the package that a component is present in, is part of the component scan.
Summary
In this article, we talked about component scan in the context of Spring and Spring Boot frameworks.The @ComponentScan annotation is used to specify packages to locate components in Spring. This is automatically done in the default package, in the case of Spring Boot.
Spring Framework
This is the first article in a series of articles on Spring Framework:
- 1 - Introduction To Spring Framework
- 2 - What Is A Dependency?
- 3 - What Is Dependency Injection?
- 4 - What Is Component Scan?
- 5 - Architecture of Spring Framework - Modularity and Spring Modules
- 6 - What Are Spring Projects?
- 7 - Introduction To Spring Batch
