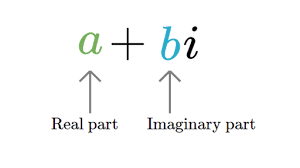Python JSON: Encode(dump), Decode(load) json Data & File (Example)
What is JSON?
JSON is a standard format for data exchange, which is inspired by JavaScript. Generally, JSON is in string or text format. JSON stands for JavaScript Object Notation.
The syntax of JSON: JSON is written as key and value pair.
{
"Key": "Value",
"Key": "Value",
}
JSON is very similar to Python dictionary. Python supports JSON, and it has an inbuilt library as a JSON.
JSON Library in Python
'marshal' and 'pickle' external modules of Python maintain a version of JSON library. To perform JSON related operations like encoding and decoding in Python you need first to import JSON library and for that in your .py file,
import json
Following methods are available in the JSON module
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| dumps() | encoding to JSON objects |
| dump() | encoded string writing on file |
| loads() | Decode the JSON string |
| load() | Decode while JSON file read |
What You Will Learn:
[hide]- What is JSON?
- JSON Library in Python
- Python to JSON (Encoding)
- JSON to Python (Decoding)
- Decoding JSON File or Parsing JSON file in Python
- Compact Encoding in Python
- Format JSON code (Pretty print)
- Complex Object encoding of Python
- Complex JSON object decoding in Python
- Overview of JSON Serialization class JSONEncoder
- Overview of JSON Deserialization class JSONDecoder
- Exceptions Related to JSON Library in Python
- Infinite and NaN Numbers in Python
- Repeated key in JSON String
- CLI (Command Line Interface) with JSON in Python
- Advantages of JSON in Python
- Implementation limitation of JSON in Python
- Cheat Code
Python to JSON (Encoding)
JSON Library of Python performs following translation of Python objects into JSON objects by default
| Python | JSON |
| dict | Object |
| list | Array |
| unicode | String |
| number - int, long | number – int |
| float | number – real |
| True | True |
| False | False |
| None | Null |
Converting Python data to JSON is called an Encoding operation. Encoding is done with the help of JSON library method – dumps()
dumps() method converts dictionary object of python into JSON string data format.
Now lets we perform our first encoding example with Python.
import json
x = {
"name": "Ken",
"age": 45,
"married": True,
"children": ("Alice","Bob"),
"pets": ['Dog'],
"cars": [
{"model": "Audi A1", "mpg": 15.1},
{"model": "Zeep Compass", "mpg": 18.1}
]
}
# sorting result in asscending order by keys:
sorted_string = json.dumps(x, indent=4, sort_keys=True)
print(sorted_string)
Output:
{"person": {"name": "Kenn", "sex": "male", "age": 28}})
Let's create a JSON file of the dictionary using the same function dump()
# here we create new data_file.json file with write mode using file i/o operation
with open('json_file.json', "w") as file_write:
# write json data into file
json.dump(person_data, file_write)
Output:
Nothing to show…In your system json_file.json is created you can check that file.
JSON to Python (Decoding)
JSON string decoding is done with the help of inbuilt method loads() & load() of JSON library in Python. Here translation table show example of JSON objects to Python objects which are helpful to perform decoding in Python of JSON string.
| JSON | Python |
| Object | dict |
| Array | list |
| String | unicode |
| number – int | number - int, long |
| number – real | float |
| True | True |
| False | False |
| Null | None |
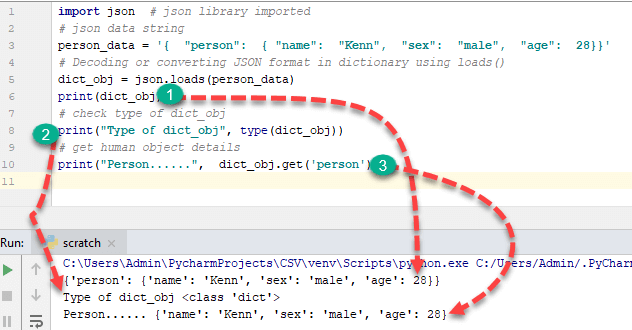
Let's see a basic example of decoding in Python with the help of json.loads() function,
import json # json library imported
# json data string
person_data = '{ "person": { "name": "Kenn", "sex": "male", "age": 28}}'
# Decoding or converting JSON format in dictionary using loads()
dict_obj = json.loads(person_data)
print(dict_obj)
# check type of dict_obj
print("Type of dict_obj", type(dict_obj))
# get human object details
print("Person......", dict_obj.get('person'))
Output:
{'person': {'name': 'Kenn', 'sex': 'male', 'age': 28}}
Type of dict_obj <class 'dict'>
Person...... {'name': 'John', 'sex': 'male'}
Decoding JSON File or Parsing JSON file in Python
NOTE: Decoding JSON file is File Input /Output (I/O) related operation. The JSON file must exist on your system at specified the location that you mention in your program.
Example,
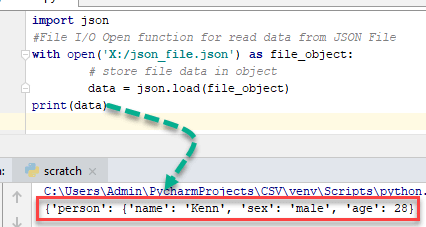
import json
#File I/O Open function for read data from JSON File
with open('X:/json_file.json') as file_object:
# store file data in object
data = json.load(file_object)
print(data)
Here data is a dictionary object of Python.
Output:
{'person': {'name': 'Kenn', 'sex': 'male', 'age': 28}}Compact Encoding in Python
When you need to reduce the size of your JSON file, you can use compact encoding in Python.
Example,
import json
# Create a List that contains dictionary
lst = ['a', 'b', 'c',{'4': 5, '6': 7}]
# separator used for compact representation of JSON.
# Use of ',' to identify list items
# Use of ':' to identify key and value in dictionary
compact_obj = json.dumps(lst, separators=(',', ':'))
print(compact_obj)
Output:
'["a", "b", "c", {"4": 5, "6": 7}]'
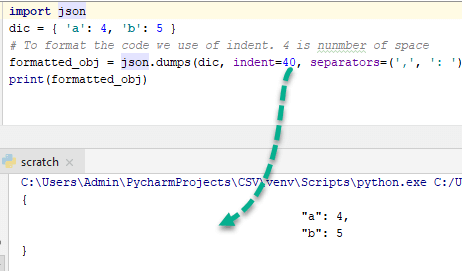
** Here output of JSON is represented in a single line which is the most compact representation by removing the space character from compact_obj ** Format JSON code (Pretty print)
- The aim is to write well-formatted code for human understanding. With the help of pretty printing, anyone can easily understand the code.
- Example,
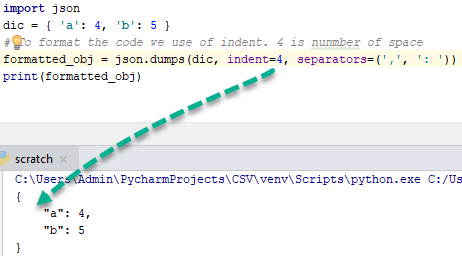
import json
dic = { 'a': 4, 'b': 5 }
''' To format the code use of indent and 4 shows number of space and use of separator is not necessary but standard way to write code of particular function. '''
formatted_obj = json.dumps(dic, indent=4, separators=(',', ': '))
print(formatted_obj)
Output:
{
"a" : 4,
"b" : 5
}
To better understand this, change indent to 40 and observe the output-
Ordering the JSON code:
sort_keys attribute in dumps() function's argument will sort the key in JSON in ascending order. The sort_keys argument is a Boolean attribute. When it's true sorting is allowed otherwise not
Example,
import json
x = {
"name": "Ken",
"age": 45,
"married": True,
"children": ("Alice", "Bob"),
"pets": [ 'Dog' ],
"cars": [
{"model": "Audi A1", "mpg": 15.1},
{"model": "Zeep Compass", "mpg": 18.1}
],
}
# sorting result in asscending order by keys:
sorted_string = json.dumps(x, indent=4, sort_keys=True)
print(sorted_string)
Output:
{
"age": 45,
"cars": [ {
"model": "Audi A1",
"mpg": 15.1
},
{
"model": "Zeep Compass",
"mpg": 18.1
}
],
"children": [ "Alice",
"Bob"
],
"married": true,
"name": "Ken",
"pets": [
"Dog"
]
}
As you may observe the keys age, cars, children, etc are arranged in ascending order.
Complex Object encoding of Python
A Complex object has two different parts that is
- Real part
- Imaginary part
Example: 3 +2i
Before performing encoding of a complex object, you need to check a variable is complex or not. You need to create a function which checks the value stored in a variable by using an instance method.
Let's create the specific function for check object is complex or eligible for encoding.
import json
# create function to check instance is complex or not
def complex_encode(object):
# check using isinstance method
if isinstance(object, complex):
return [object.real, object.imag]
# raised error using exception handling if object is not complex
raise TypeError(repr(object) + " is not JSON serialized")
# perform json encoding by passing parameter
complex_obj = json.dumps(4 + 5j, default=complex_encode)
print(complex_obj)
Output:
'[4.0, 5.0]'Complex JSON object decoding in Python
To decode complex object in JSON, use an object_hook parameter which checks JSON string contains the complex object or not. Example,
import json
# function check JSON string contains complex object
def is_complex(objct):
if '__complex__' in objct:
return complex(objct['real'], objct['img'])
return objct
# use of json loads method with object_hook for check object complex or not
complex_object =json.loads('{"__complex__": true, "real": 4, "img": 5}', object_hook = is_complex)
#here we not passed complex object so it's convert into dictionary
simple_object =json.loads('{"real": 6, "img": 7}', object_hook = is_complex)
print("Complex_object......",complex_object)
print("Without_complex_object......",simple_object)
Output:
Complex_object...... (4+5j)
Without_complex_object...... {'real': 6, 'img': 7}
Overview of JSON Serialization class JSONEncoder
JSONEncoder class is used for serialization of any Python object while performing encoding. It contains three different methods of encoding which are
- default(o) – Implemented in the subclass and return serialize object for o object.
- encode(o) – Same as json.dumps() method return JSON string of Python data structure.
- iterencode(o) – Represent string one by one and encode object o.
With the help of encode() method of JSONEncoder class, we can also encode any Python object.
# import JSONEncoder class from json
from json.encoder import JSONEncoder
colour_dict = { "colour": ["red", "yellow", "green" ]}
# directly called encode method of JSON
JSONEncoder().encode(colour_dict)
Output:
'{"colour": ["red", "yellow", "green"]}'Overview of JSON Deserialization class JSONDecoder
JSONDecoder class is used for deserialization of any Python object while performing decoding. It contains three different methods of decoding which are
- default(o) – Implemented in the subclass and return deserialized object o object.
- decode(o) – Same as json.loads() method return Python data structure of JSON string or data.
- raw_decode(o) – Represent Python dictionary one by one and decode object o.
With the help of decode() method of JSONDecoder class, we can also decode JSON string.
import json
# import JSONDecoder class from json
from json.decoder import JSONDecoder
colour_string = '{ "colour": ["red", "yellow"]}'
# directly called decode method of JSON
JSONDecoder().decode(colour_string)
Output:
{'colour': ['red', 'yellow']}Decoding JSON data from URL: Real Life Example
We will fetch data of CityBike NYC (Bike Sharing System) from specified URL(https://feeds.citibikenyc.com/stations/stations.json) and convert into dictionary format.
Example,
NOTE:- Make sure requests library is already installed in your Python, If not then open Terminal or CMD and type
- (For Python 3 or above) pip3 install requests
import json
import requests
# get JSON string data from CityBike NYC using web requests library
json_response= requests.get("https://feeds.citibikenyc.com/stations/stations.json")
# check type of json_response object
print(type(json_response.text))
# load data in loads() function of json library
bike_dict = json.loads(json_response.text)
#check type of news_dict
print(type(bike_dict))
# now get stationBeanList key data from dict
print(bike_dict['stationBeanList'][0])
Output:
<class 'str'>
<class 'dict'>
{
'id': 487,
'stationName': 'E 20 St & FDR Drive',
'availableDocks': 24,
'totalDocks': 34,
'latitude': 40.73314259,
'longitude': -73.97573881,
'statusValue': 'In Service',
'statusKey': 1,
'availableBikes': 9,
'stAddress1': 'E 20 St & FDR Drive',
'stAddress2': '',
'city': '',
'postalCode': '',
'location': '',
'altitude': '',
'testStation': False,
'lastCommunicationTime': '2018-12-11 10:59:09 PM', 'landMark': ''
}
Exceptions Related to JSON Library in Python:
- Class json.JSONDecoderError handles the exception related to decoding operation. and it's a subclass of ValueError.
- Exception - json.JSONDecoderError(msg, doc)
-
Parameters of Exception are,
- msg – Unformatted Error message
- doc – JSON docs parsed
- pos – start index of doc when it's failed
- lineno – line no shows correspond to pos
- colon – column no correspond to pos
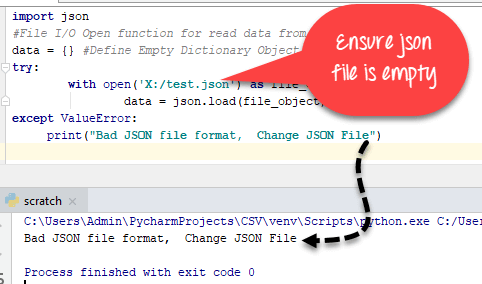
Example,
import json
#File I/O Open function for read data from JSON File
data = {} #Define Empty Dictionary Object
try:
with open('json_file_name.json') as file_object:
data = json.load(file_object)
except ValueError:
print("Bad JSON file format, Change JSON File")
Infinite and NaN Numbers in Python
JSON Data Interchange Format (RFC – Request For Comments) doesn't allow Infinite or Nan Value but there is no restriction in Python- JSON Library to perform Infinite and Nan Value related operation. If JSON gets INFINITE and Nan datatype than it's converted it into literal.
Example,
import json
# pass float Infinite value
infinite_json = json.dumps(float('inf'))
# check infinite json type
print(infinite_json)
print(type(infinite_json))
json_nan = json.dumps(float('nan'))
print(json_nan)
# pass json_string as Infinity
infinite = json.loads('Infinity')
print(infinite)
# check type of Infinity
print(type(infinite))
Output:
Infinity
<class 'str'>
NaN
inf
<class 'float'>
Repeated key in JSON String
RFC specifies the key name should be unique in a JSON object, but it's not mandatory. Python JSON library does not raise an exception of repeated objects in JSON. It ignores all repeated key-value pair and considers only last key-value pair among them.
- Example,
import json
repeat_pair = '{"a": 1, "a": 2, "a": 3}'
json.loads(repeat_pair)
Output:
{'a': 3}CLI (Command Line Interface) with JSON in Python
json.tool provides the command line interface to validate JSON pretty-print syntax. Let's see an example of CLI
$ echo '{"name" : "Kings Authur" }' | python3 -m json.toolOutput:
{
"name": " Kings Authur "
}
Advantages of JSON in Python
- Easy to move back between container and value (JSON to Python and Python to JSON)
- Human readable (Pretty-print) JSON Object
- Widely used in data handling.
- Doesn't have the same data structure in the single file.
Implementation limitation of JSON in Python
- In deserializer of JSON range and prediction of a number
- The Maximum length of JSON string and arrays of JSON and nesting levels of object.
Cheat Code
|
json.dumps(person_data) |
Create JSON Object |
|
json.dump(person_data, file_write) |
Create JSON File using File I/O of Python |
|
compact_obj = json.dumps(data, separators=(',',':')) |
Compact JSON Object by removing space character from JSON Object using separator |
|
formatted_obj = json.dumps(dic, indent=4, separators=(',', ': ')) |
Formatting JSON code using Indent |
|
sorted_string = json.dumps(x, indent=4, sort_keys=True) |
Sorting JSON object key by alphabetic order |
|
complex_obj = json.dumps(4 + 5j, default=complex_encode) |
Python Complex Object encoding in JSON |
|
JSONEncoder().encode(colour_dict) |
Use of JSONEncoder Class for Serialization |
|
json.loads(data_string) |
Decoding JSON String in Python dictionary using json.loads() function |
|
json.loads('{"__complex__": true, "real": 4, "img": 5}', object_hook = is_complex) |
Decoding of complex JSON object to Python |
|
JSONDecoder().decode(colour_string) |
Use of Decoding JSON to Python with Deserialization |