Reading and Writing CSV Files in Python using CSV Module & Pandas
What is a CSV file?
A CSV file is a type of plain text file that uses specific structuring to arrange tabular data. CSV is a common format for data interchange as it's compact, simple and general. Many online services allow its users to export tabular data from the website into a CSV file. Files of CSV will open into Excel, and nearly all databases have a tool to allow import from CSV file. The standard format is defined by rows and columns data. Moreover, each row is terminated by a newline to begin the next row. Also within the row, each column is separated by a comma.
In this tutorial, you will learn:
- What is a CSV file?
- CSV Sample File.
- Python CSV Module
- CSV Module Functions
- Reading CSV Files
- Reading as a Dictionary
- Writing to CSV Files
- Reading CSV Files with Pandas
- Writing to CSV Files with Pandas
CSV Sample File.
Data in the form of tables is also called CSV (comma separated values) - literally "comma-separated values." This is a text format intended for the presentation of tabular data. Each line of the file is one line of the table. The values of individual columns are separated by a separator symbol - a comma (,), a semicolon (;) or another symbol. CSV can be easily read and processed by Python.
Consider the following Tabe
Table Data
| Programming language | Designed by | Appeared | Extension |
| Python | Guido van Rossum | 1991 | .py |
| Java | James Gosling | 1995 | .java |
| C++ | Bjarne Stroustrup | 1983 | .cpp |
You can represent this table in csv as below.
CSV Data
Programming language, Designed by, Appeared, Extension
Python, Guido van Rossum, 1991, .py
Java, James Gosling, 1995, .java
C++, Bjarne Stroustrup,1983,.cpp
As you can see each row is a new line, and each column is separated with a comma. This is an example of how a CSV file looks like.
Python CSV Module
Python provides a CSV module to handle CSV files. To read/write data, you need to loop through rows of the CSV. You need to use the split method to get data from specified columns.
CSV Module Functions
In CSV module documentation you can find following functions:
- csv.field_size_limit – return maximum field size
- csv.get_dialect – get the dialect which is associated with the name
- csv.list_dialects – show all registered dialects
- csv.reader – read data from a csv file
- csv.register_dialect - associate dialect with name
- csv.writer – write data to a csv file
- csv.unregister_dialect - delete the dialect associated with the name the dialect registry
- csv.QUOTE_ALL - Quote everything, regardless of type.
- csv.QUOTE_MINIMAL - Quote fields with special characters
- csv.QUOTE_NONNUMERIC - Quote all fields that aren't numbers value
- csv.QUOTE_NONE – Don't quote anything in output
In this tutorial, we are going to focus only on the reader and writer functions which allow you to edit, modify, and manipulate the data in a CSV file.
How to Read a CSV File
To read data from CSV files, you must use the reader function to generate a reader object.
The reader function is developed to take each row of the file and make a list of all columns. Then, you have to choose the column you want the variable data for.
It sounds a lot more intricate than it is. Let's take a look at this example, and we will find out that working with csv file isn't so hard.
#import necessary modules
import csv
with open('X:\data.csv','rt')as f:
data = csv.reader(f)
for row in data:
print(row)
When you execute the program above, the output will be:
['Programming language; Designed by; Appeared; Extension']
['Python; Guido van Rossum; 1991; .py']
['Java; James Gosling; 1995; .java']
['C++; Bjarne Stroustrup;1983;.cpp']
How to Read a CSV as a Dictionary
You can also you use DictReader to read CSV files. The results are interpreted as a dictionary where the header row is the key, and other rows are values.
Consider the following code
#import necessary modules
import csv
reader = csv.DictReader(open("file2.csv"))
for raw in reader:
print(raw)
The result of this code is:
OrderedDict([('Programming language', 'Python'), ('Designed by', 'Guido van Rossum'), (' Appeared', ' 1991'), (' Extension', ' .py')])
OrderedDict([('Programming language', 'Java'), ('Designed by', 'James Gosling'), (' Appeared', ' 1995'), (' Extension', ' .java')])
OrderedDict([('Programming language', 'C++'), ('Designed by', ' Bjarne Stroustrup'), (' Appeared', ' 1985'), (' Extension', ' .cpp')])
And this way to read data from CSV file is much easier than earlier method. However, this is not isn't the best way to read data.
How to write CSV File
When you have a set of data that you would like to store in a CSV file you have to use writer() function. To iterate the data over the rows(lines), you have to use the writerow() function.
Consider the following example. We write data into a file "writeData.csv" where the delimiter is an apostrophe.
#import necessary modules
import csv
with open('X:\writeData.csv', mode='w') as file:
writer = csv.writer(file, delimiter=',', quotechar='"', quoting=csv.QUOTE_MINIMAL)
#way to write to csv file
writer.writerow(['Programming language', 'Designed by', 'Appeared', 'Extension'])
writer.writerow(['Python', 'Guido van Rossum', '1991', '.py'])
writer.writerow(['Java', 'James Gosling', '1995', '.java'])
writer.writerow(['C++', 'Bjarne Stroustrup', '1985', '.cpp'])
Result in csv file is:
Programming language, Designed by, Appeared, Extension
Python, Guido van Rossum, 1991, .py
Java, James Gosling, 1995, .java
C++, Bjarne Stroustrup,1983,.cppReading CSV Files with Pandas
Pandas is an opensource library that allows to you perform data manipulation in Python. Pandas provide an easy way to create, manipulate and delete the data.
You must install pandas library with command <code>pip install pandas</code>. In windows, you will execute this command in Command Prompt while in Linux in the Terminal.
Reading the CSV into a pandas DataFrame is very quick and easy:
#import necessary modules
import pandas
result = pandas.read_csv('X:\data.csv')
print(result)
Result:
Programming language, Designed by, Appeared, Extension
0 Python, Guido van Rossum, 1991, .py
1 Java, James Gosling, 1995, .java
2 C++, Bjarne Stroustrup,1983,.cpp Very useful library. In just three lines of code you the same result as earlier. Pandas know that the first line of the CSV contained column names, and it will use them automatically.
Writing to CSV Files with Pandas
Writing to CSV file with Pandas is as easy as reading. Here you can convince in it. First you must create DataFrame based on the following code.
from pandas import DataFrame
C = {'Programming language': ['Python','Java', 'C++'],
'Designed by': ['Guido van Rossum', 'James Gosling', 'Bjarne Stroustrup'],
'Appeared': ['1991', '1995', '1985'],
'Extension': ['.py', '.java', '.cpp'],
}
df = DataFrame(C, columns= ['Programming language', 'Designed by', 'Appeared', 'Extension'])
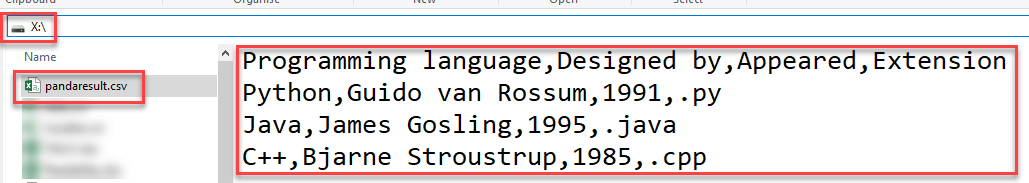
export_csv = df.to_csv (r'X:\pandaresult.csv', index = None, header=True) # here you have to write path, where result file will be stored
print (df)
Here is the output
Programming language, Designed by, Appeared, Extension
0 Python, Guido van Rossum, 1991, .py
1 Java, James Gosling, 1995, .java
2 C++, Bjarne Stroustrup,1983,.cppAnd CSV file is created at the specified location.
Conclusion
So, now you know how use method 'csv' and also read and write data in CSV format. CSV files are widely used in software applications because they are easy to read and manage, and their small size makes them relatively fast for processing and transmission.
The csv module provides various functions and classes which allow you to read and write easily. You can look at the official Python documentation and find some more interesting tips and modules. CSV is the best way for saving, viewing, and sending data. Actually, it isn't so hard to learn as it seems at the beginning. But with a little practice, you'll master it.
Pandas is a great alternative to read CSV files.
Also, there are other ways to parse text files with libraries like ANTLR, PLY, and PlyPlus. They can all handle heavy-duty parsing, and if simple String manipulation doesn't work, there are regular expressions which you can use.