Python with MySQL: Connect, Create Database, Table, Insert [Examples]
Before diving deep, let's understand
What is MySQL?
MySQL is an Open-Source database and one of the best type of RDBMS (Relational Database Management System). Co-founder of MySQLdb is Michael Widenius's, and also MySQL name derives from the daughter of Michael.
How to Install MySQL
Install MySQL in Linux/Unix:
Download RPM package for Linux/Unix from Official site: https://www.mysql.com/downloads/
In terminal use following command
rpm -i <Package_name>Example rpm -i MySQL-5.0.9.0.i386.rpm
To check in Linux
mysql --versionInstall MySQL in Windows
Download MySQL database exe from official site and install as usual normal installation of software in Windows. Refer this tutorial, for a step by step guide
Install MySQL Connector Library for Python
For Python 2.7 or lower install using pip as:
pip install mysql-connector
For Python 3 or higher version install using pip3 as:
pip3 install mysql-connector Test the MySQL Database connection with Python
To test database connection here we use pre-installed MySQL connector and pass credentials into connect() function like host, username and password.
Syntax to access MySQL with Python:
import mysql.connector
db_connection = mysql.connector.connect(
host="hostname",
user="username",
passwd="password"
)
Example,
import mysql.connector
db_connection = mysql.connector.connect(
host="localhost",
user="root",
passwd="root"
)
print(db_connection)
Output:
<mysql.connector.connection.MySQLConnection object at 0x000002338A4C6B00>
Here output shows the connection created successfully.
Creating Database in MySQL using Python
Syntax to Create new database in SQL is
CREATE DATABASE "database_name"
Now we create database using Python in MySQL
import mysql.connector
db_connection = mysql.connector.connect(
host= "localhost",
user= "root",
passwd= "root"
)
# creating database_cursor to perform SQL operation
db_cursor = db_connection.cursor()
# executing cursor with execute method and pass SQL query
db_cursor.execute("CREATE DATABASE my_first_db")
# get list of all databases
db_cursor.execute("SHOW DATABASES")
#print all databases
for db in db_cursor:
print(db)
Output:
Here above image shows the my_first_db database is created
Create a Table in MySQL with Python
Let's create a simple table "student" which has two columns.
SQL Syntax:
CREATE TABLE student (id INT, name VARCHAR(255))
Example:
import mysql.connector
db_connection = mysql.connector.connect(
host="localhost",
user="root",
passwd="root",
database="my_first_db"
)
db_cursor = db_connection.cursor()
#Here creating database table as student'
db_cursor.execute("CREATE TABLE student (id INT, name VARCHAR(255))")
#Get database table'
db_cursor.execute("SHOW TABLES")
for table in db_cursor:
print(table)
Output:
('student',) Create a Table with Primary Key
Let's create an Employee table with three different columns. We will add a primary key in id column with AUTO_INCREMENT constraint
SQL Syntax,
CREATE TABLE employee(id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY, name VARCHAR(255), salary INT(6))
Example,
import mysql.connector
db_connection = mysql.connector.connect(
host="localhost",
user="root",
passwd="root",
database="my_first_db"
)
db_cursor = db_connection.cursor()
#Here creating database table as employee with primary key
db_cursor.execute("CREATE TABLE employee(id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY, name VARCHAR(255), salary INT(6))")
#Get database table
db_cursor.execute("SHOW TABLES")
for table in db_cursor:
print(table)
Output:
('employee',) ('student',)ALTER table in MySQL with Python
Alter command is used for modification of Table structure in SQL. Here we will alter Student table and add a primary key to the id field.
SQL Syntax,
ALTER TABLE student MODIFY id INT PRIMARY KEY
Example,
import mysql.connector
db_connection = mysql.connector.connect(
host="localhost",
user="root",
passwd="root",
database="my_first_db"
)
db_cursor = db_connection.cursor()
#Here we modify existing column id
db_cursor.execute("ALTER TABLE student MODIFY id INT PRIMARY KEY")
Output:
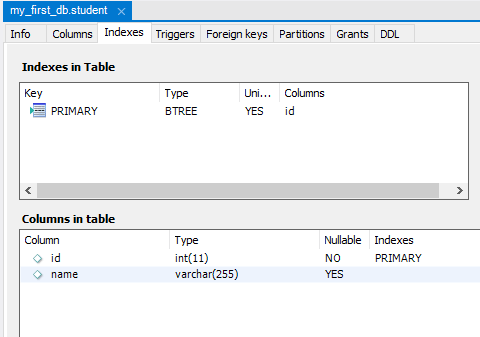
Here below you can see the id column is modified.
Insert Operation with MySQL in Python:
Let's perform insertion operation in MySQL Database table which we already create. We will insert data oi STUDENT table and EMPLOYEE table.
SQL Syntax,
INSERT INTO student (id, name) VALUES (01, "John")
INSERT INTO employee (id, name, salary) VALUES(01, "John", 10000)
Example,
import mysql.connector
db_connection = mysql.connector.connect(
host="localhost",
user="root",
passwd="root",
database="my_first_db"
)
db_cursor = db_connection.cursor()
student_sql_query = "INSERT INTO student(id,name) VALUES(01, 'John')"
employee_sql_query = " INSERT INTO employee (id, name, salary) VALUES (01, 'John', 10000)"
#Execute cursor and pass query as well as student data
db_cursor.execute(student_sql_query)
#Execute cursor and pass query of employee and data of employee
db_cursor.execute(employee_sql_query)
db_connection.commit()
print(db_cursor.rowcount, "Record Inserted")
Output:
2 Record Inserted