Spring Boot and H2 in memory database
This guide will help you understand the concept of in memory database. We will look at simple JPA example to understand the best practices in using in memory databases.
You will learn
- What is an in memory database?
- Why do you use an in memory database?
- What are the best practices in using an in memory database?
- How to connect a Spring Boot project to H2?
What is an in memory database?
Typical databases involve a lot of setup.
For example, with Oracle or mySQL databases, you would need to
- Install the Database
- Setup a Schema
- Setup the tables
- Populate the data
- Connect the application to the database by setting up a data source and a lot of other code
Scenario 1 - Let’s consider a situation where you would want to do a quick POC. Using a traditional database involves a lot of overhead.
Scenario 2 - Consider your unit tests
- You don’t want them to fail when some data/schema in the database changes
- You would want to be able to run them in parallel - multiple developers might be running the tests in parallel.
In these kind of scenarios, an in memory database provides an ideal solution.
An in memory database is created when an application starts up and destroyed when the application is stopped.
Advantages
- Zero project setup or infrastructure
- Zero Configuration
- Zero Maintainance
- Easy to use for Learning, POCs and Unit Tests
- Spring Boot provides Simple Configuration to switch between a real database and an in memory database like H2
H2
H2 is one of the popular in memory databases. Spring Boot has very good integration for H2.
From https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/H2_(DBMS)
H2 is a relational database management system written in Java. It can be embedded in Java applications or run in the client-server mode.
H2 supports a sub set of the SQL standard.
H2 also provides a web console to maintain the database.
Spring Boot and H2
You need very little configuration to connect Spring Boot application with H2.
In most situations, just adding the H2 runtime jar into dependencies should be sufficient.
<dependency>
<groupId>com.h2database</groupId>
<artifactId>h2</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
Setting up a Spring Boot Project with H2
Spring Initializr http://start.spring.io/ is great tool to bootstrap your Spring Boot projects.
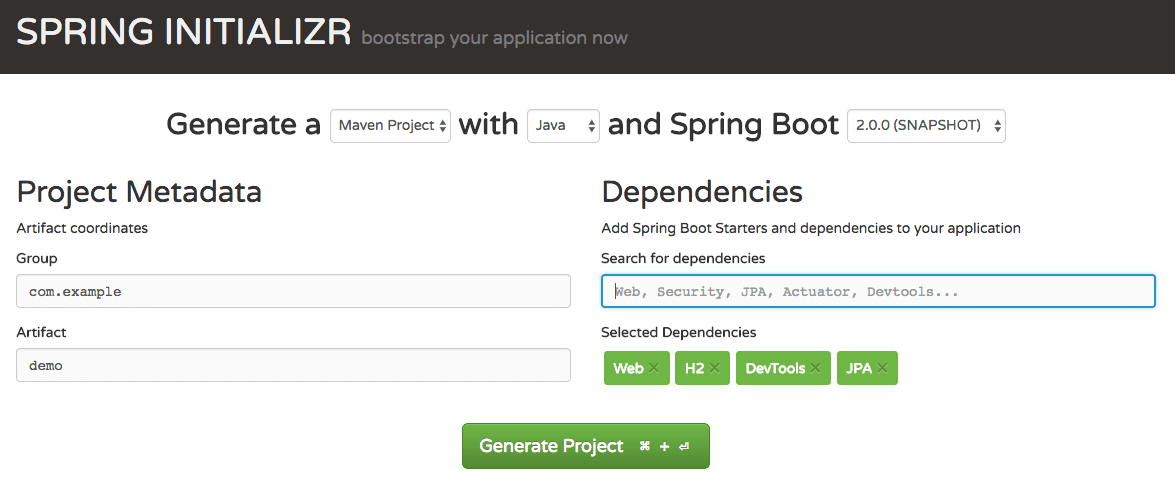
As shown in the image above, following steps have to be done
- Launch Spring Initializr and choose the following
- Choose
com.girishgodage.springboot.rest.exampleas Group - Choose
spring-boot-2-jpa-with-hibernate-and-h2as Artifact - Choose following dependencies
- Web
- JPA
- H2
- DevTools
- Choose
- Click Generate Project.
- Import the project into Eclipse. File -> Import -> Existing Maven Project.
Ensure that H2 is selected in the dependencies.
Create a simple Student Entity with a primary key id.
@Entity
public class Student {
@Id
@GeneratedValue
private Long id;
private String name;
private String passportNumber;
H2 - A Few Tips
- An in-memory database is live only during the time of execution of the application. It is an efficient way to learn a framework.
- This is not how you want your real world applications to behave.
- We explain how to connect to a database of your choice in the answer to the question “How do we connect to a external database?”.
Spring Boot and H2 Magic
H2 provides a web interface called H2 Console to see the data. Let’s enable h2 console in the application.properties.
/src/main/resources/application.properties
# Enabling H2 Console
spring.h2.console.enabled=true
When you start the application up now, you would see a lot of magic unfold!
When you reload the application, you can launch up H2 Console at http://localhost:8080/h2-console.
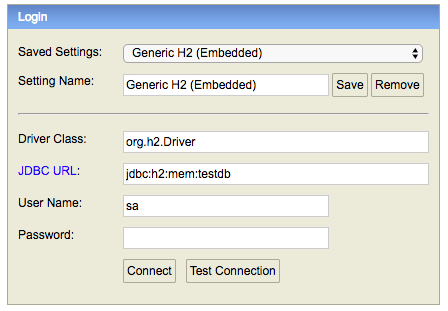
Tip - Make sure that you use
jdbc:h2:mem:testdbas JDBC URL.
You will see that a new table called ‘student’ is created in H2 Console.
How did the Student table get created?
Its because of Spring Boot Auto Configuration. We will talk about this in the next section.
You can also populate some data into student table by adding a file called data.sql
/src/main/resources/data.sql
insert into student
values(10001,'Ranga', 'E1234567');
insert into student
values(10002,'Ravi', 'A1234568');
When you reload the application, you can launch up H2 Console to see that the student table is populated with the data from `data.sql’
- http://localhost:8080/h2-console.
How did all the magic happen? Let’s look at it question by question in the next section.
Frequently asked questions about Spring Boot, JPA, Hibernate and H2
Q : How does H2 and Spring Boot combination work?
First and most important thing - Spring Boot is intelligent.
If you are talking to an in memory db, by default, it looks at the entities and creates the database and the tables.
However, if you connect to a mysql database, Spring Boot knows that its a permanent database. By default, it expects you to set up the database, set up the tables and it uses the connection that you established.
Q : How did the Spring Boot Application connect to the database H2?
Its down to Spring Boot Auto Configuration!
First thing you would need to understand is Spring Boot Auto Configuration.
As far as H2 is concerned, as soon as Spring Boot sees H2 in the class path, it auto configures a data source similar to what you see below:
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:h2:mem:testdb
spring.datasource.driverClassName=org.h2.Driver
spring.datasource.username=sa
spring.datasource.password=
spring.jpa.database-platform=org.hibernate.dialect.H2Dialect
It knows that you are using an inmemory database H2 and it uses the default url if you don’t provide one.
Q : Where is the database connection info specified? How does it know to automatically connect to H2?
Thats Spring Boot Autoconfiguration magic.
From https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/current/reference/html/using-boot-auto-configuration.html
Spring Boot auto-configuration attempts to automatically configure your Spring application based on the jar dependencies that you have added. For example, If HSQLDB is on your classpath, and you have not manually configured any database connection beans, then Spring Boot will auto-configure an in-memory database.
Q : What happens if H2 is not in the classpath?
You get this error
Cannot determine embedded database driver class for database type NONE
Add H2 to the pom.xml and Restart your server
<dependency>
<groupId>com.h2database</groupId>
<artifactId>h2</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
Q : Why is the data lost between restart?
H2 is an in memory database. Its not a persisted database.
H2 is a great tool for learning because you need zero setup.
Error : Table is not created automatically in h2 embedded db or I’m unable to see the tables
Usually, the table’s are created but the url used in H2 GUI Console is wrong.
In the browser, change the database url to jdbc:h2:mem:testdb (Shown in the screen below).
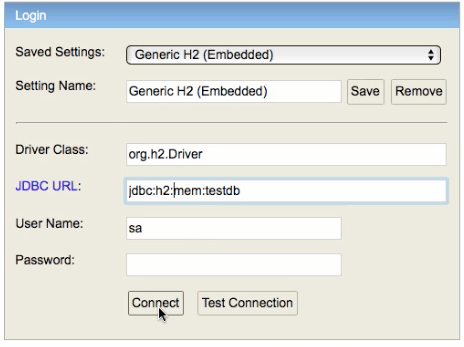
You should be good to go!
Error : H2 Console is not Launched up?
Try enabling it in the application.properties
spring.h2.console.enabled=true
Q : How did the insert query from data.sql run at application startup?
That’s part of the Spring Boot startup routine. Any queries in data.sql are run at application startup. You can read more here.
- https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/current/reference/html/howto-database-initialization.html
Running H2 as a persisted database with Spring Boot
While we dont recommend this , it interesting to note that H2 has a persisted database mode
- With this configuration, the data is not lost even after spring boot restart and computer restart.
You would find H2 being very rarely used in this way. If you are really interested in a persistent database, we recommend exploring MySQL, Oracle or some other relational database.
application.properties
spring.datasource.name=yourdbname
spring.datasource.driverClassName=org.h2.Driver
spring.datasource.initialize=false
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:h2:file:~/yourdbname;DB_CLOSE_ON_EXIT=FALSE;IFEXISTS=TRUE;DB_CLOSE_DELAY=-1;
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto = update
Using H2 for unit tests
The standard properties file that Spring Boot picks up automatically when running an application is called application.properties and resides in the src/main/resources folder.
If we want to use different properties for tests, then we can override the properties file in the main folder by placing another file with the same name in src/test/resources.
The application.properties file in src/test/resources folder should contain the standard key-value pairs necessary for configuring a in memory connection.
First add the dependencies for your database driver (mysql in the example below) and make the dependency for h2 test scoped.
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.h2database</groupId>
<artifactId>h2</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
Use the mysql database for your real code
src\main\resources\application.properties
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=none
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/person_example
spring.datasource.username=personuser
spring.datasource.password=YOUR_PASSWORD
Use in memory database for your unit tests
src\test\resources\application.properties
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=org.h2.Driver
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:h2:mem:testdb;DB_CLOSE_DELAY=-1
spring.datasource.username=sa
spring.datasource.password=sa
