When & How Node.JS Should be Used ?
If Node.js has ever been on your mind –– or you’ve recently started learning it –– you might be asking yourself: where can I use Node.js? If the stats are to be believed, among three in four software engineers incorporate node either in the full stack or in the backend. With the thumping majority of apps using the popular JS run-time environment, it’s a great opportunity to understand all existing Node.js use case and implement it in your organization.
So you are starting your next project, and you have decided to use Node.js. Well, what this means for you is to first thoroughly read the documentation and then to ask around in the community that uses Node.js.
But here’s the catch –– thanks to its countless use cases, researching Node.js inevitably proves to be tedious and time consuming. And you realise, a little too late, that you’ve signed-up for a never-ending research loop.
The way out of this loop lies in understanding the Node.js use case like ––
- Leverage data streaming with Node.js
- Implementing web-scraping with Node.js
- Building a proxy-server using Node.js
So, why use Node.js, you ask?
TL;DR
Key points addressed in this article
- Node.js – What is it used for?
- Node.js Usage: How the best use case of Node.js are categorized
- Node.js use case Infographic
- 10 Industries that can leverage their business with these use cases
- When should you not use Node.js?
-
Node.JS – What is it used for?
Built on Chrome’s V8 JavaScript engine, Node.js is an asynchronous event-driven JavaScript runtime. By using the event-callback/non-blocking approach, Node.js offers a single-threaded event-io model that allows orchestration of tasks running in parallel. It supports multiple connections without a need for a large memory footprint.
The usage of Node.js is not only limited to building web applications, but also for implementing various kinds of services.
- Backends and servers
- Frontends
- Developing API
- Microservices
- Scripting and automation
Now that we know about some uses of Node.js, let’s understand how these uses are categorized.
Node.js Usage: How the best use case of Node.js are categorized
We analyzed 10 industries that use Node.js in their tech stack and classified them into different categories. The loyalty matrix attached below is the result of our analysis as to how often Node.js gets used category wise and what’s the retention percentage of these categories.
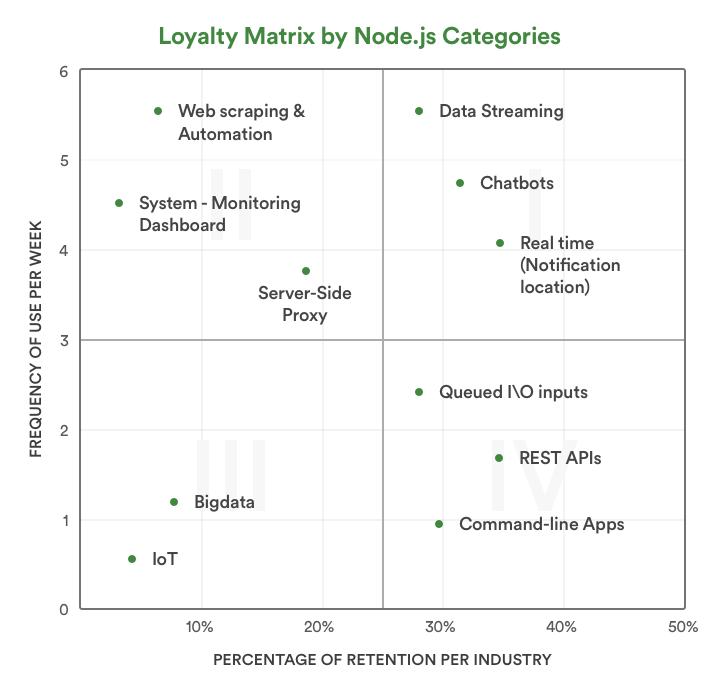
Quadrant I includes categories that are most frequently used and to which Industries are leveraging them over time. Not surprisingly, Data streaming, Chatbots, and real-time data fall within this quadrant. Industries use Node.js for these categories every day, many times a day.
Quadrant II consists of categories that are used intensely, but for finite periods of time. Web scraping falls within quadrant II, along with server-side proxy and a system monitoring dashboard. Although these categories are used by Industries in an intensive manner, the retention over a period of time is less than those falling in Quadrant I.
Quadrant III is made up of categories that have low retention and infrequent use. However, the use of Node.js in these categories is expected to increase in the upcoming years. Needless to say, Big-data and IoT technology fall in this quadrant.
Quadrant IV comprises of categories that have a low frequency of use, but a loyal Industry base. The categories like REST API, Queued I/O Inputs, and command-line apps fall in the category.
Let’s cover these categories one-by-one.
1. Data Streaming
The Problem
Streaming data in web require heavy processing
Data streaming is a complex process because it requires a continuous stream of data to be generated by an array of different sources and devices, delivered in a wide myriad of formats.
The Solution
Node.js streams make data-streaming easier than ever
In traditional Media streaming, HTTP requests and responses are treated like isolated events; however, in reality, they are streams. Node.js can be used to build some cool data streaming features where files can still be processed while they’re being uploaded. This is possible because data comes in through a stream and can be processed online without being interrupted. For instance: real-time audio or video encoding is possible, particularly with the JavaScript library such as Node. Media and Entertainment is such an industry where Node.js can be utilized in Data streaming.
2. Server-side proxy
The Problem
Third-party proxies can cause troubles in building complex web-apps
Third-party proxy services such as Nginx and HAProxy are sometimes not feasible and scalable in handling multiple requests from various sources at a time.
The Solution
Node.js makes it easier to build a proxy server
While third-party proxy services such as Nginx or HAProxy are affordable, they can add to severe complexity when used for building large scale websites. Node.js can be easily employed as a server-side proxy for collecting data from various third-party resources. Whether you are building a news websites such as BBC, a media website such as Forbes, and entertainment websites such as IMDb, you would want to load content from various third-party domains. Node.js is beneficial for proxying different services with different response times. When used as a server-side proxy, it is capable of handling a large number of simultaneous connections in a non-blocking manner.
For instance: consider a website such as BBC news communicating with various third-party resources, gathering data from different sources, or storing assets like images and videos to third-party cloud services.
3. Big Data and Analytics
The Problem
Dealing with large data in a browser is troublesome
If you are trying to deal with larger data in the browser, then it might wait for your users for a long time. Any user does not like to wait for more than 5 minutes with a frozen browser, no matter how cool the analysis might be.
The Solution
Node.js back pressuring makes data processing easier
Node.js streams allow to effectively have a pipeline from which data starts at one point and flows through until the end. To overcome the problem of dealing with larger data, it is important to have a mechanism for breaking the large data into multiple chunks. Using back pressuring, which comes from implementing Node.js, you can use a computer’s resources while processing very large sets of data.
4. Wireless Connectivity
The Problem
Bandwidth consumption and bi-directional signaling
Bandwidth consumption is a major challenge for IoT connectivity. For collecting and routing data between devices, reliable bidirectional signaling is essential. This is a challenge as it requires a reliable server to collect the data and send it to a particular destination.
Solution
Node.js server ensures data connectivity without any request blockage
Node.js is the best solution to create a proxy server for data connectivity and routing as it supports I/O connectivity without blocking.
Some JavaScript libraries for Node.Js such as Node-Red, NodeMcu, and Node Serialport offer ready-made solutions for connecting IoT devices.
5. System Monitoring Dashboard
The Problem
Pushing real-time data at scale can be inconvenient
Dashboards are meant to convey a large amount of information quickly, however, finding the relevant information and displaying it in real-time is difficult. While using a dashboard to respond to errors, there are high chances for you to encounter several problems like:
- You won’t be automatically notified of unusual behavior.
- You’ll need to monitor the dashboard to detect potential errors continuously.
The Solution
Pushing data in real-time with Node.JS is easy
Using the advance capability of event loop in Node.js, you can build a powerful web-based dashboard that validates the status of all services in an asynchronous manner. The data can be pushed in real-time to clients using WebSockets. By using Node.js, both internal (intra-company) and public services’ statuses can be reported live. For instance, you can build a dashboard to monitor real-time data which runs on frameworks backed by Node.js and Websocket instead of Java or Java Applets.
6. Real-time Data
The Problem
Scalability bottlenecks in real-time data is very common
The common real-time data streaming issues are sizing and scaling. If your web app is running live 24 x 7, there is a need to plan out extra resources to execute all the operations without failing to meet any service-level agreements.
The Solution
Node.JS makes real-time data a boon for web apps
Node.js is a good fit for building real-time web apps by using push technology over web sockets (a two-way communication between the servers and clients). What’s more revolutionary about Node.js is that it is the best choice for creating server-side web apps. Let’s walk you through a few reasons as to why it is pivotal to choose Node.js for building real-time web apps:
- Sharing & Reusing: It lets developers share the package of library code.
- I/O Bound: Node.js handles I/O bound tasks effectively.
- Fast & Scalable: In real-time web apps, it is possible to handle the multi-users requests due to the single-threaded model of Node.js.
The collaborative web apps (Trello, Google Docs), live chat, instant messaging, and online gaming are examples of real-time apps that benefit from Node.js architecture. These apps do function within a time frame that the users recognize as immediate and current.
7. Queued I/ O Inputs
The Problem
An app database can be crashed with huge data load
Receiving a high amount of concurrent data can make database congested and resulting in the crash of the application. Also, it becomes expensive to queue data and maintain concurrency because of huge data load.
The Solution
The asynchronous nature of Node.js makes it capable of handling huge data load
Due to the asynchronous capability and event-driven architecture, Node.js excels in handling huge data load. What’s more, the data can be queued through caching or messaging queuing infrastructure such as RabbitMQ or ZeroMQ and stored in different database batch-write process.
8. Chatbots
The Problem
For businesses, investment in customer service calls is costly
A typical business spends $1.3 trillion on 265 billion customer service calls each year. Moreover, 265 billion customer support requests are made every year, which costs businesses a whopping $1.3 trillion to service them. That’s a huge cost considering the revenue made by these businesses is not constant.
The Solution
Chatbots can offer better customer service experience at a lower cost
Building chatbots with Node.js is a perfect solution because you can build a simple API quickly with hapi.js, Express, etc as it supports real-time messages (RTM) or Slack RTM bots. Facebook has built a sample chatbot with Node.js, which is available on Github.
Drift (conversion-driven marketing and sales platform) is another example of chatbot that connects businesses with the best leads. Drift lets users to directly message them within the browser or provide them an automated chat experience.
9. Web Scraping & Automation
The Problem
Manual data extraction is a cumbersome process
Extracting millions of data from different website sources is not possible manually. Furthermore, data analytics often gets challenging to implement in this case, considering the amount of data required to push through the stream.
The Solution
Data scraping with Node.js is a cheaper alternative
An automated way of collecting information or extracted data from websites called as data scraping. Node.js embraces a vast library of packages that simplify tasks such as web scraping. For web scraping, there are mainly two packages used i.e., request and cheerio in Node.js.
The request package is used for downloading web pages. On the other hand, cheerio generates a DOM (Document Object Model) tree and provides a subset of jQuery function set to manipulate it.
10. REST API
The Problem
SOAP makes API Integration a complex process
Although SOAP (Simple Object Access Protocol) has a high capacity of data transfer, API integration with it becomes very complex.
The Solution
Building REST API with Node.js speeds up the API Integration process
The trendiest usage of Node.js also covers building RESTful APIs for API Integration. REST APIs, which can be developed using Express.js in Node, is commonly used in enterprise software development project. Moreover, the current trend of microservices design patterns has made the use of RESTful APIs even more common.
11. Command-line
Another area where Node.js excels is developing command-line apps. You must be wondering why should we choose Node.js to build command-line apps? The main reason is the strong Node.js ecosystem means that the hundreds of thousands of packages are available for all purposes. They are specifically designed to help build powerful command-line tools.
Building command-line apps with Node.js is simple, fast, and extremely cost-effective, thanks to the libraries like commander, yargs, and oclif. Node.js empowers developers who are not familiar with backend languages to use JavaScript outside the web and build diverse work automation solutions.
