In this article, we focus on Spring Cloud. We will talk about the various components under its umbrella.
You will learn
- What is Spring Cloud?
- What are the typical challenges in microservices architectures?
- What are the challenges that Spring Cloud solves?
- What are the important projects under Spring Cloud umbrella?
- How does Spring Cloud help you build your microservices architecture?
Introducing Spring Cloud
If you go to the homepage of Spring Cloud:
Spring Cloud provides tools for developers to quickly build common patterns in distributed systems.
Spring Cloud is not a single project, rather a cluster of them.
Shown below is just a small sample of the projects present under this umbrella.
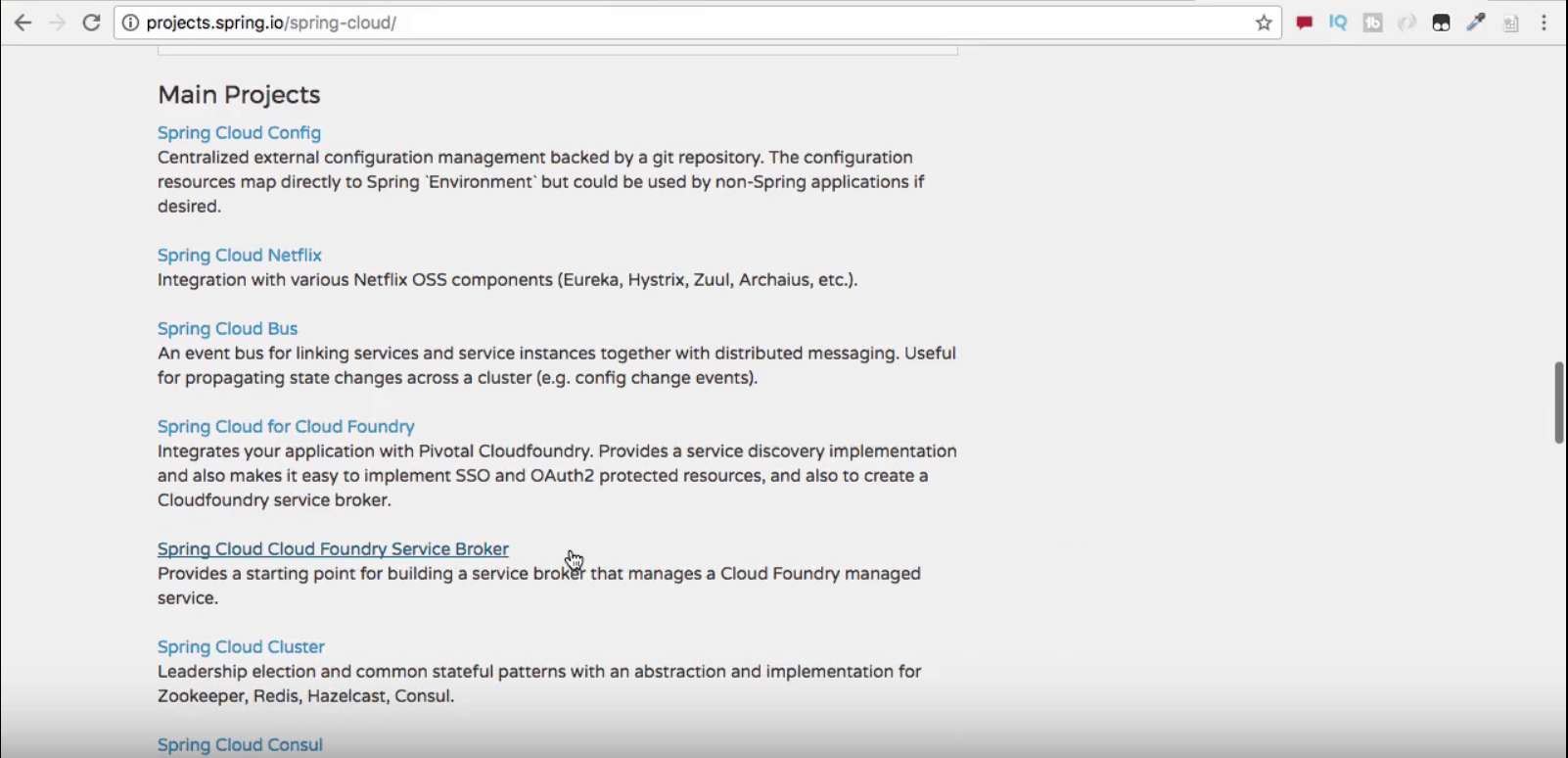
Let’s get a quick introduction to some of the important projects under Spring Cloud umbrella
Spring Cloud Netflix
Netflix was one of the first organizations to play around with microservices architecture. Under this project, a large number of projects have been open sourced for public use. Eureka, Hystrix and Zuul are popular ones among them.
Spring Cloud Config
This project provides a framework for centralized configuration management, making use of a Git or a SVN repository.
Spring Cloud Bus
This enables the microservices and infrastructure components to communicate with each other, in a distributed setup.
Challenges in Microservices Architectures
Let’s now have a look at the challenges we face while developing microservices applications, and the solutions offered by Spring Cloud for them.
Configuration Management
In a system with a microservices architecture, there are a large number of small-sized microservices that communicate with each other:
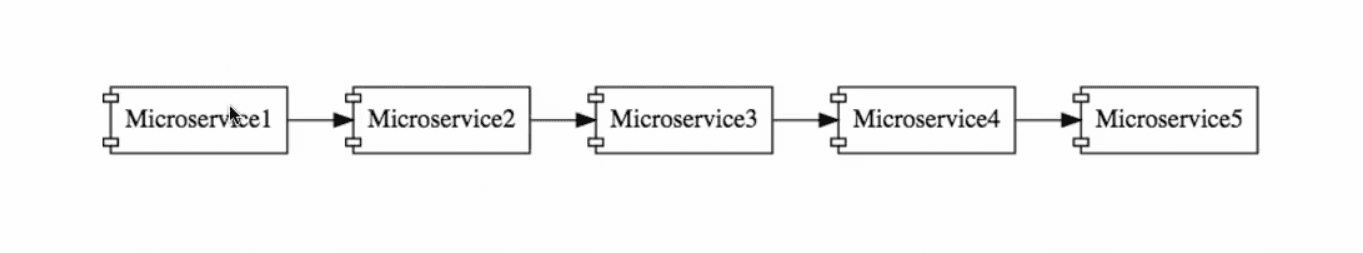
Each of these microservices needs to execute across multiple environments. In a given environment, there could be multiple instances of that microservice running. This means the operations team needs to manage a lot of configuration information for each microservice.
The Spring Cloud Config Server provides a solution to such configuration management
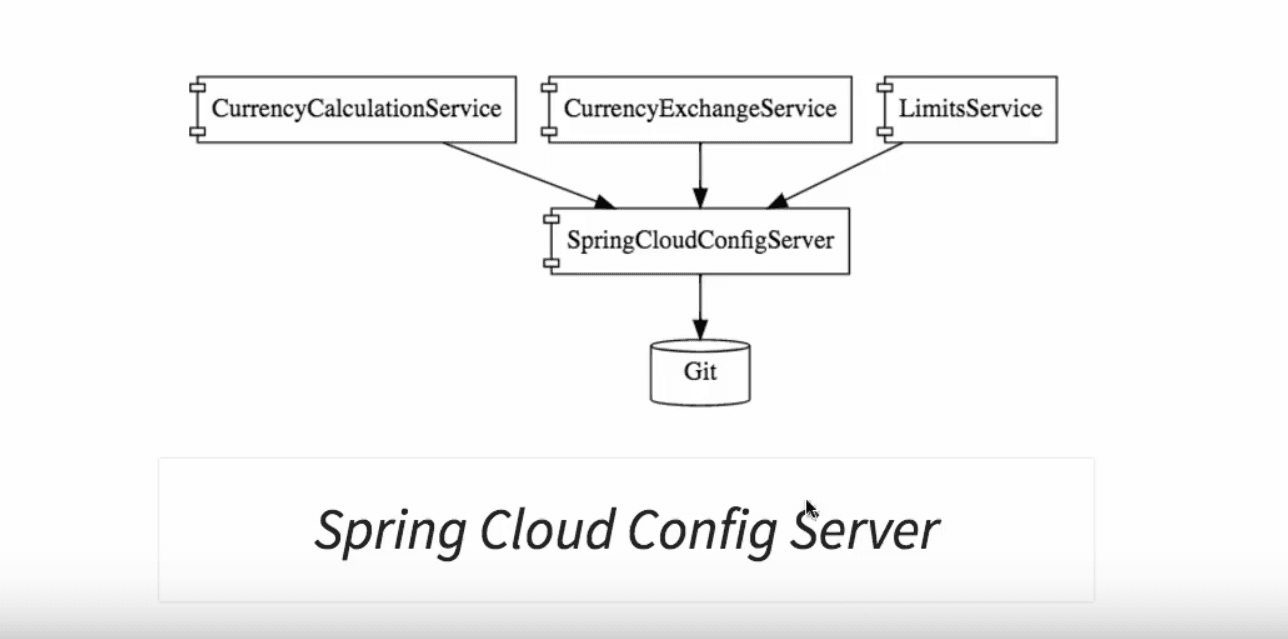
It provides an approach, where all the configurations across environments for all the microservices, is stored in a Git repository. The Spring Cloud Config Server then exposes this information to all the microservices. Storing the configurations in such a centralized location makes it easier for the operations team to manage it.
Dynamic Scale Up And Down
Consider the following example:
The CurrencyCalculationService microservice talks to another microservice, the CurrencyExchangeService. Currently, three instances of CurrencyExchangeService are running. it is possible that at any point in time, more instances can be added in, or existing instances can be removed.
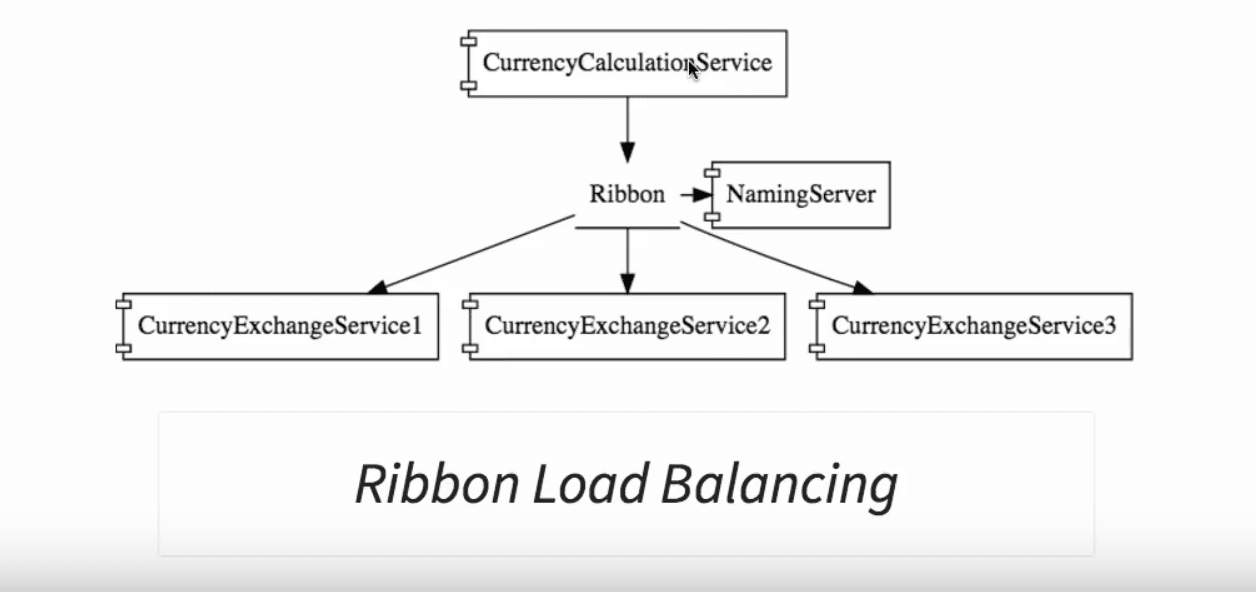
We need the CurrencyCalculationService to be able to distribute the load across the instances available at that point in time.
The need is to dynamically find out the number of instances of the CurrencyExchangeService at that time, and distribute the load across them.
Service Registration
The solution which Spring Cloud provides involves using a naming server - Eureka - with which all instances of each microservices that are created, register themselves. This first step is called service registration.
Service Discovery
The second step is service discovery. In the example above, the CurrencyCalculationService can ask the Eureka naming server, about the instances of the CurrencyExchangeService that are running. The naming service would, in turn, provide the URLs of those instances back to the CurrencyConversionService. This helps establish a dynamic relationship between instances of the communicating microservices.
Load Balancing
A related step is load balancing, for which the client side load balancing framework, Ribbon, is available. The CurrencyCalucationService would post ribbons, and the load of the events would be evenly distributed across instances of the CurrencyExchangeService.
The Feign framework helps us to write simpler RESTful clients.
Visibility And Monitoring
In Microservices Architectures, You would need to have complete visibility into what’s happening in your microservices.
When you use Spring Cloud Sleuth, you assign an ID to a request across multiple components.
Zipkin Distributed tracing is used to trace a request as it travels through the system.
Gateway
A significant point about systems with microservices architecture is that the services have a lot of common features. These include security, logging, analytics, and so on. It is not practical to implement each of these common features in every single microservice.
An API Gateway provides a great solution to this kind of a challenge.
The Netflix Zuul API gateway is a great solution to implement an API Gateway.
Fault Tolerance
When any service in the system is down, a fault tolerance service helps provide a default response to requests, until the service is restored.
Hystrix is the fault tolerance framework made available by Spring Cloud.
Summary
In this article, we had a look at the Spring Cloud project, and saw that it is an umbrella for a wide variety of frameworks. Each of these solves a particular problem associated with microservices. Important problems include service registration, service discovery, load distribution, event tracing, service monitoring and fault tolerance.
Introduction to Cloud, Microservice - Challenges and Advantages
This is the article in a series of five articles on cloud and microservices:
- 1 - Microservices Architecutres - Quick introduction to Cloud - Why, What and How?
- 2 - Microservice Architectures - Introduction to Spring Cloud
- 3 - Microservices Architectures - Advantages Of Microservices
- 4 - Microservice Architectures - Challenges with building Microservices
- 5 - Microservices Architectures - Microservices vs SOA
