How to Build an E-commerce App using Node.js ?
React, Angular, and Vue –– all these frontend frameworks are good for building eCommerce applications. But what about Backend? Node.js is one such framework that allows you to build scalable eCommerce backends. This article provides you all the necessary information you need to use Nodejs in eCommerce web application development.

Whether it be React.js, Vue.js, and Angular.js, we love them all! ❤️
However, building web applications involves a lot more complex processing at the server-side, let alone the frontend of the application. Here’s why we thought to share our knowledge regarding building eCommerce applications.
Although our article on building a scalable web application covers a lot about modeling complex interfaces, today we will take a step forward to understand how to build an eCommerce app with Nodejs.
Let’s begin with the top reason to consider Node.js as a technology to develop complex and scalable eCommerce applications. Thereafter, we’ll walk you through the options you should have while using node in eCommerce web applications.
Table of Content
- The Truth about eCommerce, no one tells you!
- Building a Nodejs eCommerce website: what are your options?
- Building a Nodejs eCommerce app with MEAN/ MERN stack
- Building a Nodejs eCommerce app with Microservices architecture
The Truth about eCommerce, no one tells you!
The best eCommerce backends in the world are designed for scalability, for they are always in charge of generating, maintaining and delivering the information to the frontend displays of a user.
The backend of your eCommerce application, however, can be either homogeneous or heterogeneous and comprises of 2 parts: the database (where the data or information is stored) and a server (which connects the data with the browser).
The Problem
Building a scalable, complex eCommerce interface is hard!
When your eCommerce business critically depends on elements such as payment gateways, logistics, suppliers, shipping etc, it induces more complexity for you to maintain high performance and availability 24×7.
Integrating most of these elements can slow down crucial activities, limiting your website’s performance. Behind the scenes (preferable at the backend), there will be hundreds or thousands of requests that are instantly pinged around the world to carry out such kinds of complex operations.
There’s a lot more going on in those few seconds; there’s a lot more that can go wrong with your website in those few seconds.
Note that, the backend of your application is one of the most critical part of any website. In most complex websites, the frontend depends gravely on the backend.
“The frontend of a website depends gravely on the backend.”
So, if the backend of a website fails due to complexity, the frontend will fall apart. As simple as that!
The Real Problem: slow backend load time
At times, a lot of developers focus on improving the frontend performance of an eCommerce to rectify these things. The real bottleneck, however, remains the slow backend load time.
So, if you have a slow backend, the only thing that your users will see on your site is a white screen (which is due to the backend tasks are not completed). The heavier your load, larger would be the backend load time. Also at some point, it may get skyrocketed to a certain extent that the application becomes unstable.
Furthermore, a *study done by Moz *shows that a slow backend load time (which is also referred to as Time to First Byte) can have a serious impact on your Search engine rankings.
A good rule of thumb is that back end load time should take no more than 20% of your total load time. A good back end load time to aim for is 200ms or less.
Nodejs to the Rescue
Building an eCommerce app with Nodejs makes a lot more sense because it ensures the balance between frontend and backend load time due to its asynchronous nature.
Here’s a graph which illustrates the importance of Asynchronous programming in improving the backend load time of an eCommerce website:
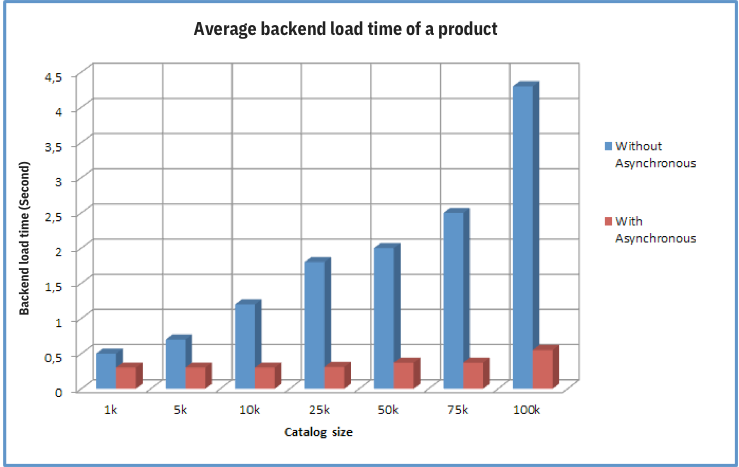
Notice how using Asynchronous communication in web apps saves you alot on backend load time.
In web applications such as eCommerce where you have huge catalog of products , going asynchronous makes a lot more sense. The good news is that Node.js allows you to use Asynchronous programming and make things easy for you.
What’s more, Node gives you an ability to handle multiple concurrent users at a time.
The reason being it be single-threaded and its event-driven architecture.
This is unlikely the case with other web technologies, which creates an additional thread for each request. This eats up the whole memory until the processing gets over.
Node.js help developers to make the best use of event loop and callbacks for I/O operations. The event loop is the classic Node.js’s way of breaking the long-running request into smaller chunks.
What heartbeat is to heart, event-loop is to Nodejs.
Node.js will keep on checking a work queue every few milliseconds, which is a great way to queue and process new tasks simultaneously at the same time. Here’s why it can be possible for your backend to serve hundreds of thousands or even a million concurrent users.
Node.js can also improve the website loading time in eCommerce.
According to a Google Study, “40% of people abandon a website that takes more than 3 seconds to load and a 1-second delay in page response can result in a 7% reduction in conversions.”
Put another way, every time your website gets slow — you might be losing out on tons of conversions.
After all, it’s been said clearly,
When your site is eCommerce, EVERY SINGLE SECOND MATTERS. Period.
PayPal has an interesting story of how they migrated from Java to Node.js which provided the site an 100% increase in business availability, even with huge load. After using Node.js, in its backend, PayPal experienced a 35% decrease in the average response time for the page which made the startup time 200ms faster.
Here’s a more statistical yet graphical representation of the results achieved by Paypal through their migration to Nodejs:
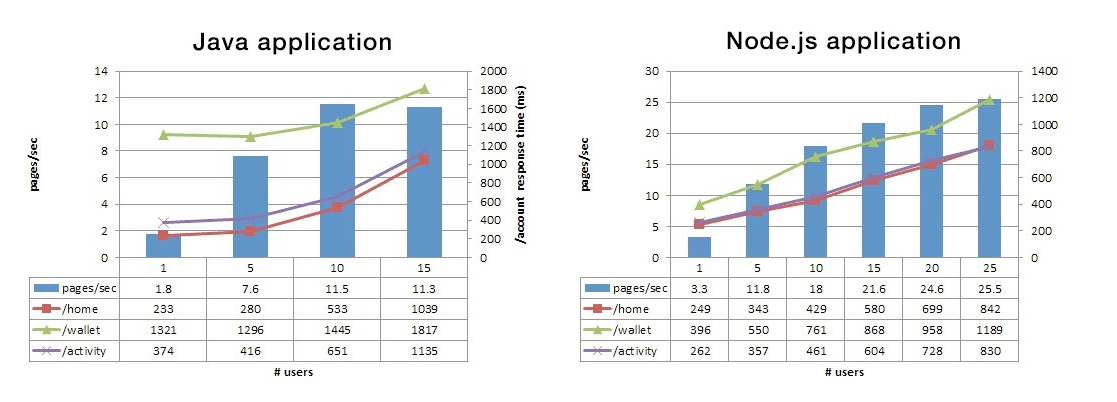
Another way of improving the startup time of your Node.js app is by turning on Gzip compression. It greatly decreases the bundled size of your app hence contributing to the increase in speed.
Building a Nodejs eCommerce website: what are your options?
Now that we have covered what goes behind the screens while developing a node eCommerce website, let’s throw some light on the options you may have with Node.js.
Building a Nodejs eCommerce app with MEAN/ MERN stack The MEAN stack works brilliantly for building an eCommerce web app. We’ll briefly explain what the MEAN stack is all about. Take a look!
MEAN and MERN stack with Nodejs: The definition
MongoDB: A NoSQL database that provides data storage and NodeJS allows server running continuously.
Express.js: A back-end web framework that enables you to create web applications by providing a simpler interface.
Angular.js/React.js: A front-end web framework that simplifies web development by providing automatic view/model synchronization. Unlike Angular, React is not a framework, it is a library.
Node.js: A JavaScript runtime built on Chrome’s V8 JS engine. It uses an event-driven and non-blocking I/O model, which makes it lightweight and efficient.
The MEAN/ MERN stack Architecture for eCommerce
MEAN and MERN stack offers you free and open-source javascript framework.
If you are just starting out to build a Node.js eCommerce website for some relevant users (say up to 10k users), either MEAN or MERN stack would be a good choice.
Here’s what goes behind the scenes while building a Nodejs eCommerce website with MEAN stack:
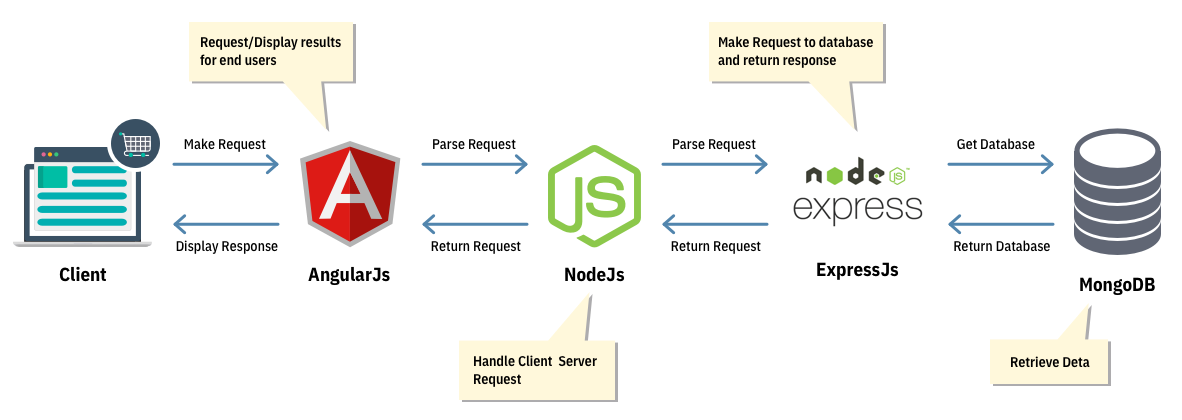
- Initially, it begins with Angular.js where all the requests emerging from the client-side are processed.
- Once the initial phase is over, the request enters to Node which is in control of the server-side.
- The request enters to Express.js where it requests for database access.
- MongoDB collects the entire data once the request is accepted and relays it to Express.js
- Express relays the response to Node which sends it to Angular.
An ideal eCommerce app is when it can respond quickly to usage spikes. When building an ecommerce site with MEAN/ MERN stack, you will be able to serve an abundance of at least 10k users, which is an ideal number for your business at the stage of inception. Valued for its scalability, flexibility, and consistency, the MEAN stack is a strong choice for developing eCommerce apps with Node because of its ability to provide concurrency and stability at the same time.
If you are curious to know about building an eCommerce web app with Reactjs (or with MERN stack), we have already covered it before. You can even go-through this amazing blog on building an eCommerce PWA with React, thank us later.
Building a NodeJS eCommerce App with Microservice Architecture
Although MEAN/MERN stacks are the best for building monolithic eCommerce applications when your business is at an early stage. There might be some situations when your eCommerce web app requires to handle millions of users.
Nodejs based Microservices Architecture to the rescue
Nodejs and Microservices are a match made in heaven! Nodejs truly complements microservices as it supports several microservice frameworks such as Seneca.js.
Instead of going for monolithic applications that require heavy maintenance, you can simply deploy a microservices-based eCommerce app that simply breaks down several functionalities into a small suite of services integrating via APIs. This kind of approach empowers multiple services (like payments and products) of your eCommerce business and let them update and scale separately.
For instance, you might deploy a product metadata service that retrieves (or periodically cache) metadata for a particular product. Moreover, you also can have a product pricing service that retrieves the product’s price for a given customer.
Aesthetically, you can have several microservices that are exposed to clients via REST APIs. Your web application can communicate with these REST APIs through an API gateway.
The following diagram shows an example of eCommerce-oriented backend microservices architecture:
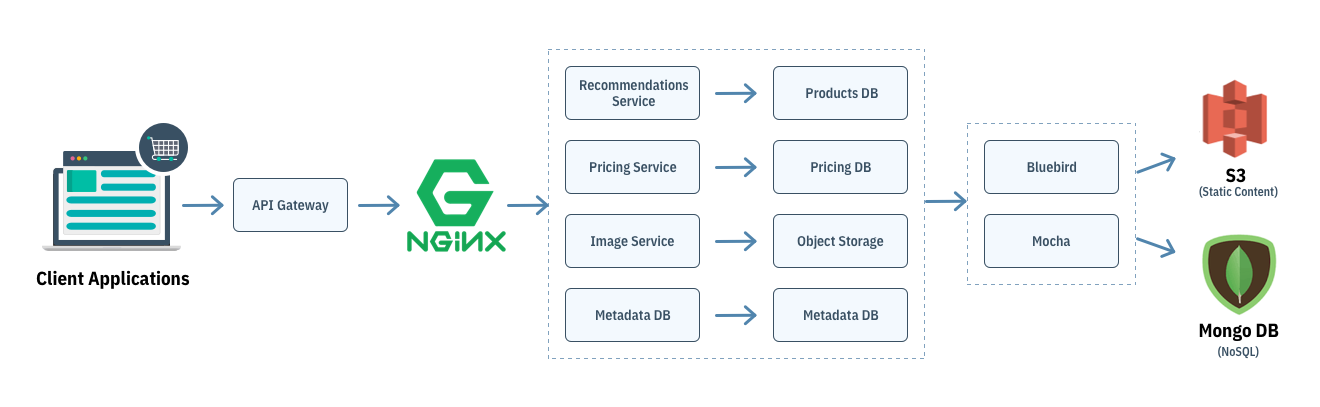
Cadenza, a subscription-based eCommerce platform, migrated its Nodejs app from MEAN stack to a micro-service based architecture. While they were using MEAN stack, they faced a hard time managing 125 different APIs in different categories such as product management, user management, payment management, etc. Even worse, problems like repetitive application crashes and huge-costs were taking a toll on their eCommerce business.
By adopting the microservices architecture pattern, they got an opportunity to code services independent of programming language and database. It simply eliminates any long-term commitment to the technology stack. What’s more, it helped them to cut down huge costs on operations.
However, Candanza is not only the eCommerce business that moved to the microservice architecture, but there are also a lot more examples. eBay, the renowned eCommerce marketplace, employed microservices architecture and scaled beyond 1 billion of users. There’s no way an eCommerce business can be scaled to such an extent with a basic architecture.
Conclusion
We possess expertise in building Node.js applications using MEAN stack. We find MEAN stack to be more convenient and easiest to learn and implement. However, we also recommend Microservices to our clients who already have built monoliths and need more scalability. Microservice architecture puts our developer in the state of a 100% control over the individual services, which is necessary when you want to build scalable kinds of stuff. With this article, we stressed the reasons why building an eCommerce web app with Nodejs is the need of the hour and what are the ways of building it.
