Amazon DynamoDB – A Complete Guide
DynamoDB is a fully managed NoSQL database service provided by Amazon. These days, databases have become the backbone for any company irrespective of how big they are. Traditional database systems which were initially used, are not the go-to solution today because of the dynamic change in requirements and type of data procured. In this Amazon DynamoDB tutorial, I will be discussing the new and fast way of storing and retrieving data using DynamoDB.
In this Amazon DynamoDB tutorial, I will be discussing the following topics:
- What Is DynamoDB?
- Terminologies Associated With DynamoDB
- Accessing Amazon DynamoDB
- Features Of DynamoDB
- DynamoDB API
- DynamoDB: Case Studies
- Demo: Creating, Inserting And Querying A Table In DynamoDB
What Is DynamoDB?
Amazon DynamoDB is a fully managed NoSQL service that works on key-value pair and other data structure documents provided by Amazon. It requires only a primary key and doesn’t require a schema to create a table. It can store any amount of data and serve any amount of traffic. With DyanmoDB, you can expect a good performance even when it scales up. It is a very simple and small API that follows key-value method to store, access and perform advanced data retrieval.
DynamoDB comprises of three fundamental units known as table, attribute, and items. A table holds a set of items, an attribute is the simplest element that stores data without any further division and item holds a set of attributes.
Now that you know what is DynamoDB, let’s move further in this Amazon DynamoDB tutorial and introduce you to the terms used here.
Terminologies Associated With DynamoDB
Here with DynamoDB, everything is kept simple, the terms used with DynamoDB are easy to understand which makes it unique from the rest of the Database services. The terms used are as follows:
- Table, Items, and Attributes
- A table can be visualized as a group of items. Taking an example of Employee records, you will have Employee Name, Employee ID, Address and Phone Number all such items will be stored in a table.
- An item is a set of attributes in a table. You can also understand an item as a set of attributes that can uniquely define your entry in a table. For example, an item in Employee records will identify a single employee.
- An attribute is a single field that is attached to an item. E.g. Employee Name.
-
Primary Key
A primary key is a unique attribute that is necessary while creating a table, it cannot be null at any given point. Hence, while inserting an item into the table, a primary key attribute is a must. E.g. Employee ID is the primary key for the table Employee records. Two items cannot have a similar primary key. DynamoDB supports two types of Primary key.
-
Simple Primary Key A simple primary key is also known as Partition key, this is basically a single attribute. DynamoDB uses Partition key’s value to distinguish items in a table. E.g. Employee ID in Employee records table.
-
Composite Primary Key A composite primary key is also known as Partition key and Sort key. This type of key is generally made up of two items. The primary component is the Partition key and the secondary component is the Sort key. E.g.* Car Details table with Brand name and Model number as a composite primary key*.
-
-
Secondary Index
A secondary index can be understood as the attribute that lets you query the data, with or without the help of a Primary key. DynamoDB has these secondary indexes that help you achieve this additional access. - DynamoDB Streams This is an additional/optional feature provided by DynamoDB to keep a track of data modification events in a table. Here, each event is represented by a stream record and if this service is enabled, then you get a new event every time when there is a new item created, an item is updated or an item is deleted.
These are the different terms used, without any further delay let’s proceed with the DynamoDB tutorial and find out how to access a table.
Accessing Amazon DynamoDB
Accessing DynamoDB is very easy and can be done using the following methods:
- Console You can access DynamoDB simply by clicking here.
- CLI(Command Line Interface) Using CLI, you can simply open your command prompt and type the relevant commands and access the table. For more details, click here.
- Using API Using AWS SDKs you can make the most of DynamoDB. AWS SDK supports a variety of languages like Java, JavaScript, .NET, Python, PHP etc. For more details, click here.
Features Of DynamoDB
DynamoDB is a NoSQL database service. DynamoDB is designed in such a way that the user can get high-performance, run scalable applications that would not be possible with the traditional database system. These additional features of DynamoDB can be seen under the following categories:
- On-demand capacity mode: The applications using the on-demand service, DynamoDB automatically scales up/down to accommodate the traffic.
- Built-in support for ACID transactions: DynamoDB provides native/ server-side support for transactions.
- On-demand backup: This feature allows you to create a complete backup of your work at any given point of time.
- Point-in-time recovery: This feature helps you with the protection of your data in case of accidental read/ write operations.
- Encryption at rest: It keeps the data encrypted even when the table is not in use. This enhances security with the help of encryption keys.
DynamoDB API
DynamoDB is a database tool and to interact with an application, it requires API. The APIs in DynamoDB are:
#### Control Plane Control Plane consists of operations responsible for “Creating” and “Managing” a DynamoDB table. The API operations that can be used are as follows:
- CreateTable: Creates a new table.
- DescribeTable: Provides information about the table.
- ListTable: Returns all the table names in your list.
- DeleteTable: Deletes the table and all its dependencies from DynamoDB.
#### Data Plane Data Plane consists of “CRUD” operation, i.e. “Create”, “Read”, “Update”, and “Delete” options to perform different actions on your table. Here in Data Plane, there are multiple operations that can be done on a table. The operations here are as follows:
- Creating Data
- PutItem: You can write a single data item to your table with the help of Primary key.
- BatchWriteItem: It is a better version of PutItem, with this you can write upto 25 items to your table.
- Reading Data
- GetItem: It retrieves a single item from a table with the help of the primary key.
- BatchGetItem: The better version of GetItem it can retrieve upto 100 items from multiple tables.
- Query: It is basically a command that retrieves an item which has a specific partition key.
- Scan: Works in a similar way as Query but doesn’t require partition key aslo it works on a specific table.
- Updating Data
- UpdateItem: It modifies a single or multiple data items in a table with the help of Primary Key.
- Deleting Data
- DeleteItem: It deletes a single item from the table with the help of Primary Key.
- BatchWriteItem: The better version of DeleteItem it can delete upto 25 items in a table.
-
DynamoDB Stream DynamoDB Stream is nothing but a service used to track data stream that is loaded into a table and retrieved from a table. To modify the streaming, the user can use the following commands:
- ListStream: It gives a list of all streams.
- DescribeStream: It gives detail about the stream and the resources used.
- GetShardIterator: It gives a Shard iterator that is a data structure to store information about the stream.
- GetRecords: Using Shard iterator GetRecords retrieves information about streams.
So, now that you have a decent idea about the different APIs supported by DynamoDB. Let’s take a look at the different case studies where customers have benefited with DynamoDB.
DynamoDB: Case Studies
I have listed down the case studies of some big companies and startups, as to how they benefited using DynamoDB.
#### 1. MLB Advanced Media MLBAM said in one of their reviews about Amazon DynamoDB that it helped them to scale up the support for games on a single day, DynamoDB also helped them to power the queries and support for fast data retrieval. #### 2. Expedia Expedia’s real-time analytics application collects data for test & learn experiments. This experiment processed nearly 200 million messages daily, they stated that DynamoDB was easy to setup and the monitoring was easier and scaling was smooth and that’s the reason they moved to using DynamoDB. #### 3. Nexon Nexon stated that they used Amazon DynamoDB as their primary database for blockbuster mobile game HIT. They stated that Nexon’s HIT leveraged DynamoDB to deliver a steady latency to deliver a fantastic mobile gaming experience.
This is how the trending NoSQL database “Amazon DynamoDB” helped companies to reach the pinnacle of user experience. Let’s move further in this Amazon DynamoDB tutorial and see how to implement the different queries.
Demo: Creating, Inserting And Querying A Table In DynamoDB
Let’s find out how to create a table in DynamoDB.
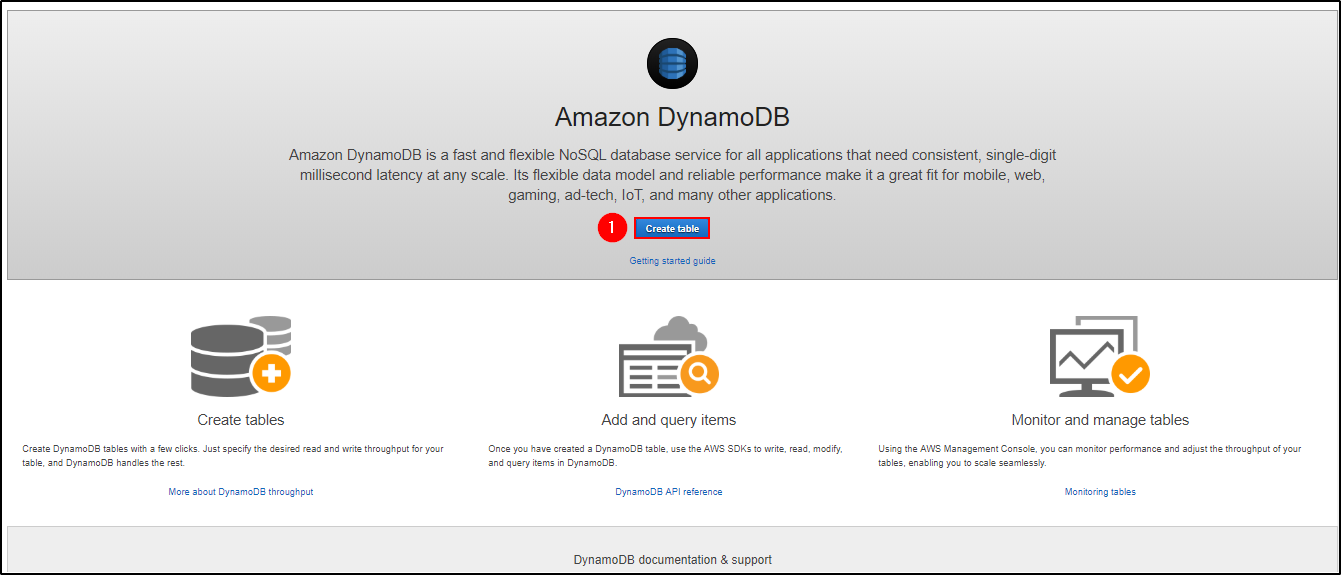
Step 1: Navigate to the DynamoDB section in AWS or click here. Select “Create Table”.
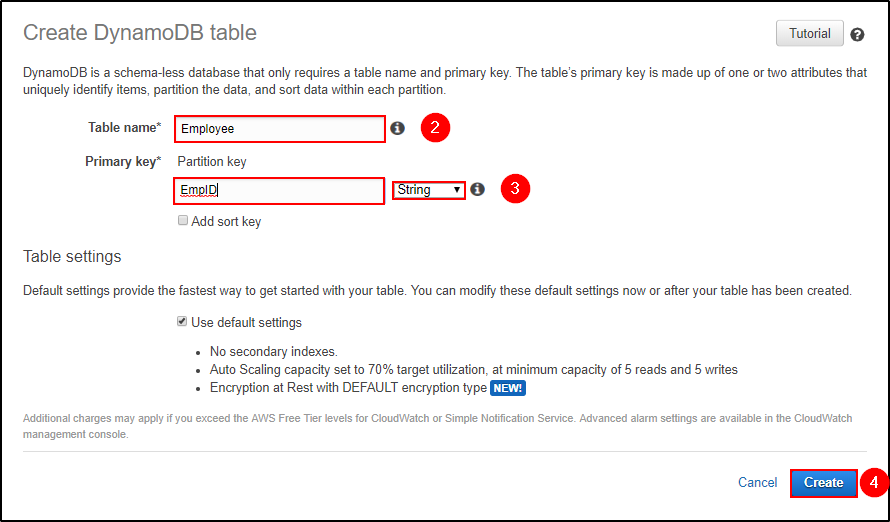
Step 2: Fill in with the necessary details and click on “Create”.
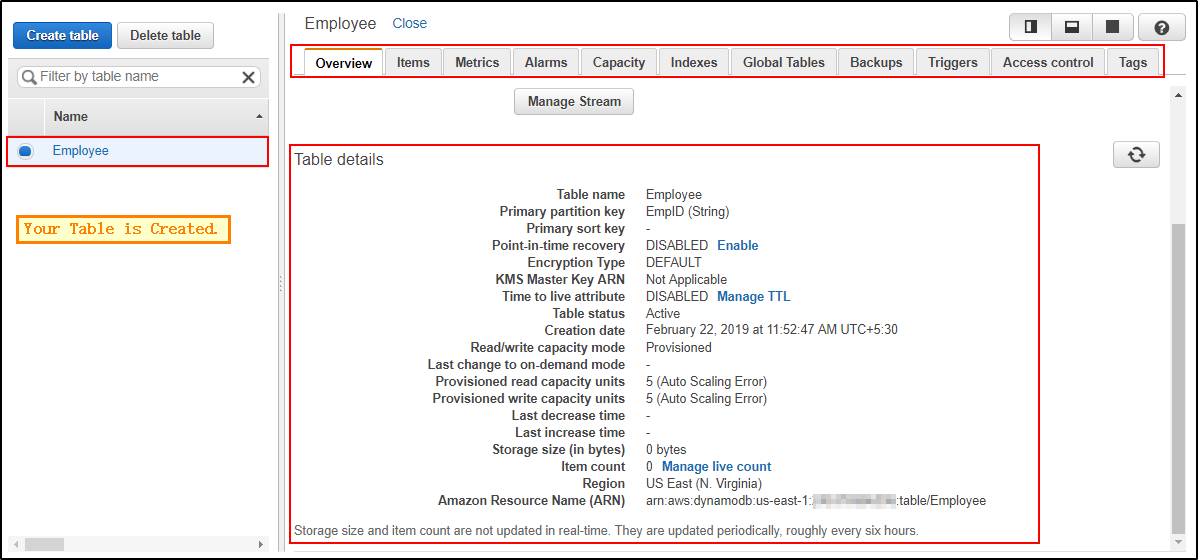
Step 3: You can view your table being created. Click on “Overview” to understand your table, click on “Items” to edit, insert and query on the table. There are many more options you can use to understand your table better.
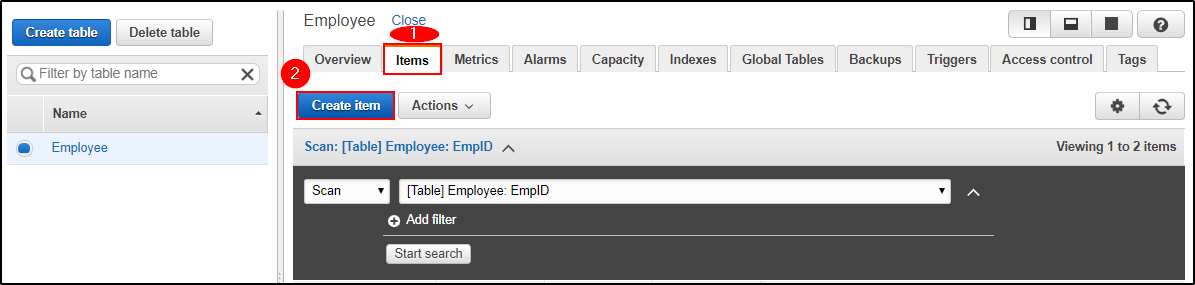
Now that you have created a table, let’s go ahead and insert a few items and understand how NoSQL works.
Step 1: Navigate to “Items” and click on “Create item”.
Step 2: It will open a JSON file where you can add different items. Click on the “+” symbol and select “Append” and select what type of data you want to enter.
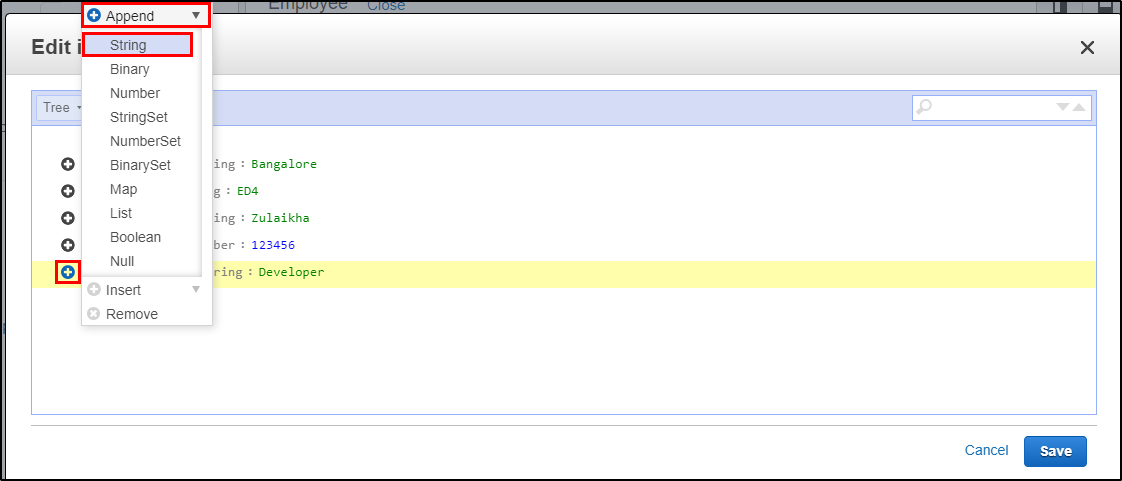
Step 3: This is what it looks like after adding multiple columns to your table. Click on “Save”
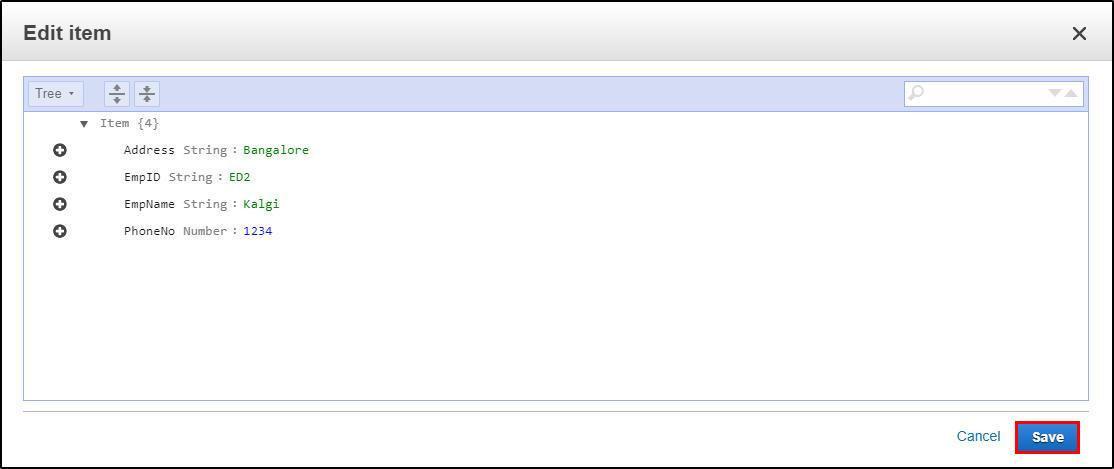
Step 4: Since it is a NoSQL architecture, you can play around with the columns you add to the table. E.g. “Position”.
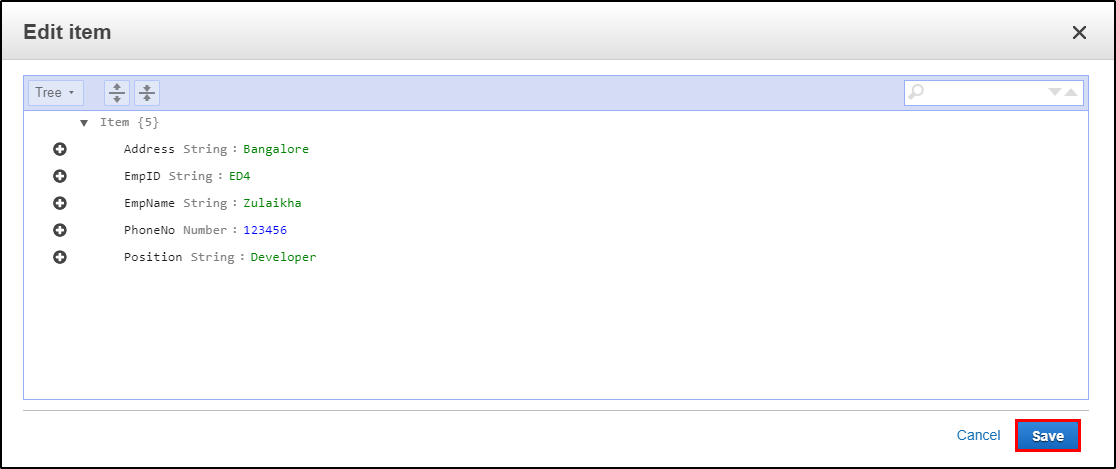
Step 5: This is how your table will look like once you have inserted the data.
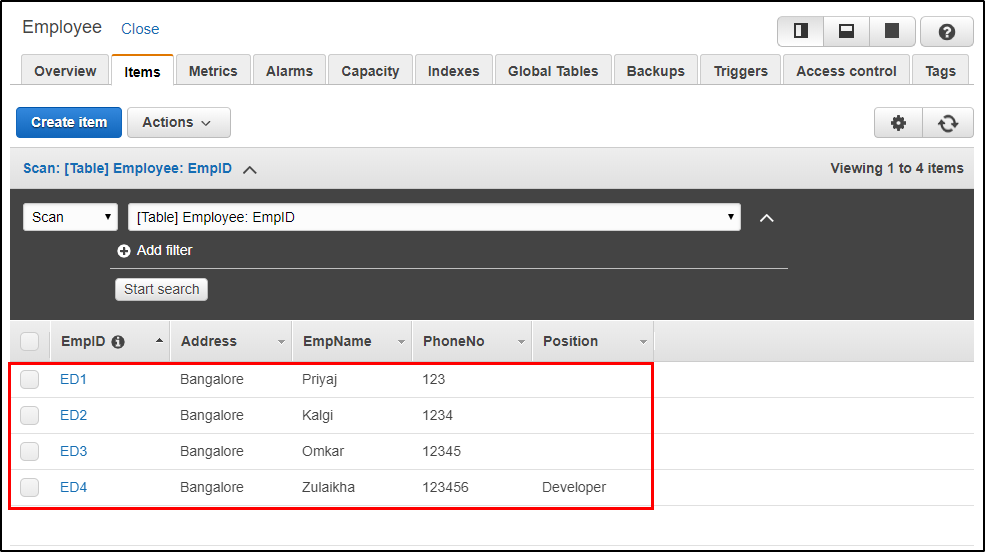
Now that we have a table ready, let’s go ahead and look at some basic queries.
Step 1: Here you can frame your query and click on “Start Search” to get the desired result.
E.g. I am searching for all the mobile numbers that are greater than or equals to “1234”.
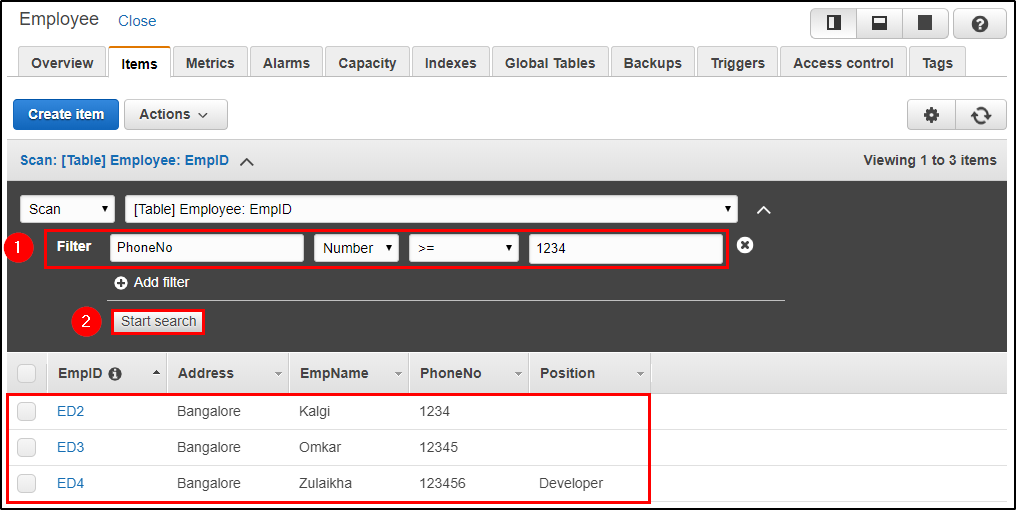
Step 2: Here, I am searching for the record which has EmpId as “ED4”.
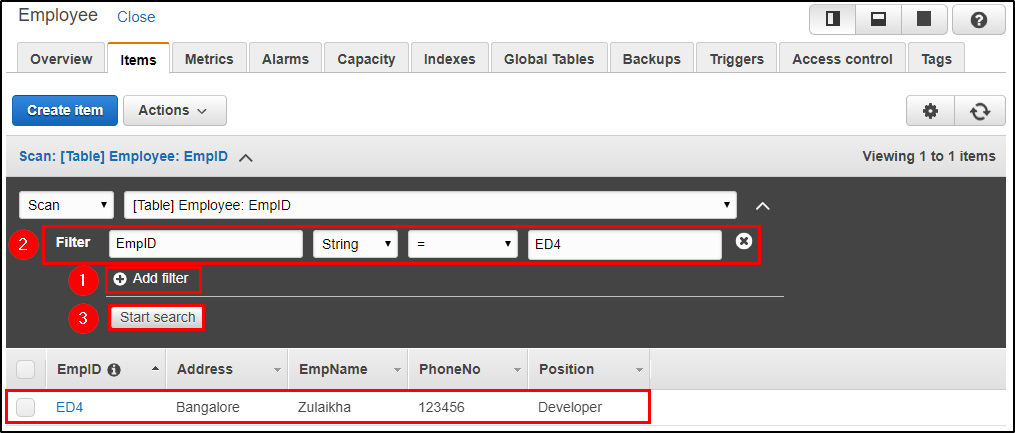
This is a small tutorial on how to use DynamoDB to suffice your needs. I hope you found this Amazon DynamoDB tutorial informative.
